- TOP CITIES
- New Delhi
- Gurgaon
- Pune
- Mumbai
- Bengaluru
- Kolkata
- Hyderabad
- Ahmedabad
- Chennai
- Indore
- Lucknow
- Jaipur
- Chandigarh
- Bhopal
- Noida
- Navi Mumbai
- Surat
- Patna
- Ludhiana
- Bhubaneshwar
- ALL CITIES
- Abohar
- Adad
- Adilabad
- Adoni
- Adsaidnakda
- Agar
- Agartala
- Agra
- Ahmedabad
- Ahmednagar
- Aizawl
- Ajmer
- Akola
- Aksjdhbaskjda
- Alappuzha
- Aligarh
- Alipurduar
- Alirajpur
- Allahabad
- Almora
- Alwar
- Ambala
- Ambattur
- Ambedkar Nagar
- Amravati
- Amreli
- Amritsar
- Amroha
- Anand
- Anantapur
- Ananthnag
- Anantnag
- Angamally
- Angul
- Ankleshwar
- Annur
- Anuppur
- Arakkonam
- Arambag
- Arantangi
- Araria
- Arcot
- Ariyalur
- Arwal
- Asansol
- Asdbakda
- Ashok Nagar
- Assaudh
- Attuvampatti
- Auraiya
- Aurangabad Bihar
- Aurangabad Maharashtra
- Aviyur
- Ayyangarkulam
- Azamgarh
- Badlapur
- Bagalkot
- Bageshwar
- Baghpat
- Bagpat
- Bahadurgarh
- Bahraich
- Baksa
- Balaghat
- Balangir
- Baleswar
- Ballia
- Bally
- Balrampur
- Banaskantha
- Banda
- Bangalore
- Bangalore Rural
- Banka
- Bankura
- Banswara
- Barabanki
- Baramati
- Baramulla
- Baran
- Baraut
- Bardhaman
- Bareilly
- Bargarh
- Barmer
- Barnala
- Barpeta
- Barrackpore
- Baruipur
- Barwani
- Basirhat
- Bastar
- Basti
- Bathinda
- Beawar
- Beed
- Begumganj
- Begusarai
- Behraghora
- Behrampur
- Belgaum
- Bellary
- Belur
- Bengaluru
- Betul
- Betul Ganj
- Bhadrak
- Bhadravati Karnataka
- Bhagalpur
- Bhandara
- Bharatpur
- Bharuch
- Bhatkal
- Bhavani
- Bhavnagar
- Bhilai
- Bhilwara
- Bhind
- Bhiwadi
- Bhiwandi
- Bhiwani
- Bhojpur
- Bhopal
- Bhubaneshwar
- Bhuna
- Bhusawal
- Bidar
- Bijapur Chattisgarh
- Bijapur Karnataka
- Bijnor
- Bikaner
- Bilaspur Chattisgarh
- Bilaspur Himachal Pradesh
- Birbhum
- Bishnupur
- Boisar
- Bokaro
- Bongaigaon
- Bongaon
- Botad
- Boudh
- Budaun
- Budgam
- Bukkapatnam
- Bulandshahr
- Buldana
- Buldhana
- Bundi
- Burdwan
- Burhanpur
- Buxar
- Cachar
- Calicut
- Chamarajanagar
- Chamba
- Chamoli
- Champawat
- Champhai
- Chandauli
- Chandel
- Chandigarh
- Chandrapur
- Changanassery
- Changlang
- Chatra
- Chennai
- Chhatarpur
- Chhindwara
- Chikkaballapur
- Chikkaballapura
- Chikmagalur
- Chintamani
- Chitradurga
- Chitrakoot
- Chittoor
- Chittorgarh
- Chrompet
- Churachandpur
- Churu
- Cochin
- Coimbatore
- Cooch Behar
- Cuddalore
- Cuddapah
- Cuttack
- Dadra & Nagar Haveli
- Dahanu
- Dahod
- Dakshina Kannada
- Daman
- Damoh
- Dans
- Dantewada
- Darbhanga
- Darjiling
- Darrang
- Datia
- Dausa
- Davangere
- Debagarh
- Dehradun
- Delhi
- Deoghar
- Deoria
- Dera Bassi
- Devanahalli
- Dewas
- Dhakaoli
- Dhalai
- Dhamtari
- Dhanbad
- Dhar
- Dharmapuri
- Dharwad
- Dhemaji
- Dhenkanal
- Dholpur
- Dhone
- Dhubri
- Dhule
- Dhully
- Dibang Valley
- Dibrugarh
- Dibrugarh Tamil Nadu
- Dimapur
- Dindigul
- Dindori
- Dispur
- Diu
- Doda
- Dombivli
- Dombivli Station
- Dumka
- Dungarpur
- Durg
- Durgapur
- East Champaran
- East Garo Hills
- East Godavari
- East Kameng
- East Khasi Hills
- East Midnapore
- East Nimar
- East Siang
- East Sikkim
- East Singhbhum
- Ellanaickenpatti
- Ernakulam
- Erode
- Etah
- Etawah
- Faizabad
- Faridabad
- Faridkot
- Farrukhabad
- Fatehabad
- Fatehgarh Sahib
- Fatehpur
- Fazilka
- Fewf
- Fewp
- Firozabad
- Firozpur
- Gadag
- Gadarwara
- Gadchiroli
- Gajapati
- Gandhinagar
- Ganganagar
- Gangtok
- Ganjam
- Garhwa
- Gariaband
- Gautam Buddha Nagar
- Gaya
- Ghaziabad
- Ghazipur
- Gir Somnath
- Giridh
- Goa
- Goalpara
- Gobichettipalayam
- Godda
- Golaghat
- Golaniya
- Gonda
- Gondia
- Gopalganj
- Gopalmath
- Gorakhpur
- Greater Noida
- Greater Thane
- Gulbarga
- Gumla
- Guna
- Guntur
- Gurdaspur
- Gurgaon
- Guwahati
- Gwalior
- Hailakandi
- Halol
- Hamirpur Himachal Pradesh
- Hamirpur Uttar Pradesh
- Hansi
- Hanumangarh
- Hapur
- Harapanahalli
- Harda
- Hardoi
- Haridwar
- Hassan
- Hathras
- Haveri
- Hazaribag
- Hazaribagh
- Hdhd
- Hinauti
- Hindaun
- Hingoli
- Hisar
- Hojai
- Hooghly
- Hosakote
- Hoshangabad
- Hoshiarpur
- Hoskote
- Hospet
- Hosur
- Howrah
- Hubli
- Hyderabad
- Ichalkaranji
- Idukki
- Imphal
- Imphal East
- Imphal West
- Indore
- Itanagar
- Jabalpur
- Jagatsinghapur
- Jaintia Hills
- Jaipur
- Jaisalmer
- Jajapur
- Jalandhar
- Jalaun
- Jalgaon
- Jallipatti
- Jalna
- Jalore
- Jalpaiguri
- Jammu
- Jamnagar
- Jamshedpur
- Jamtara
- Jamui
- Janjgir-Champa
- Jashpur
- Jaunpur
- Jayamala
- Jehanabad
- Jhabua
- Jhai
- Jhajjar
- Jhalawar
- Jhansi
- Jhargram
- Jharsuguda
- Jhujhunu
- Jind
- Jodhpur
- Jorhat
- Junagadh
- Jyotiba Phule Nagar
- Kachchh
- Kadamakkudy
- Kadapa
- Kadiri
- Kadthal
- Kaghaz Nagar
- Kaimur Bhabua
- Kaithal
- Kakinada
- Kalahandi
- Kalipahari
- Kallakurichi
- Kalligudi
- Kalyani
- Kamal
- Kamrup
- Kanadukathan
- Kanchipuram
- Kandhamal
- Kandukur
- Kangra
- Kanker
- Kannauj
- Kannur
- Kanpur
- Kanpur Dehat
- Kanpur Nagar
- Kansapuram
- Kanyakumari
- Kapurthala
- Kar
- Karad
- Karaikal
- Karaikudi
- Karatholuvu
- Karauli
- Karbi Anglong
- Kargil
- Karimganj
- Karimnagar
- Karnal
- Karupatti
- Karur
- Karwar
- Kasaragod
- Kathua
- Katihar
- Katni
- Kattupakkam
- Kaushambi
- Kavaratti
- Kawardha
- Kendrapara
- Kendujhar
- Khagaria
- Khammam
- Khandwa
- Khanna
- Kharagpur
- Khargone
- Kheda
- Kheri
- Khorda
- Kichha
- Kinnaur
- Kiphire
- Kishanganj
- Kochi
- Kodagu
- Kodaikanal Observatory
- Koderma
- Kohima
- Kokrajhar
- Kolar
- Kolasib
- Kolhapur
- Kolkat
- Kolkata
- Kollam
- Kooram
- Koppal
- Koraput
- Korba
- Koriya
- Kota
- Kothakudi
- Kothur
- Kottayam
- Kovilpatti
- Koyilandy
- Kozhikode
- Krishna
- Krishnagiri
- Kulgam
- Kullu
- Kumbakonam
- Kumburvayal
- Kundli
- Kupwara
- Kurnool
- Kurukkalpatti
- Kurukshetra
- Kurung Kumey
- Kushinagar
- Kutch
- Laddivadi
- Lahul & Spiti
- Lakhimpur
- Lakhisarai
- Lakshadweep
- Lalitpur
- Lambakheda
- Latehar
- Latur
- Lawngtlai
- Leh
- Lohardaga
- Lohit
- Lonavala
- Longleng
- Lower Dibang Valley
- Lower Subansiri
- Lucknow
- Ludhiana
- Lunglei
- Machur
- Madhepura
- Madhubani
- Madhupur
- Madikeri
- Madurai
- Mahabubabad
- Mahabubnagar
- Mahadanapuram
- Maharajganj
- Mahasamund
- Mahbub Nagar
- Mahe
- Mahendragarh
- Mahoba
- Mainaguri
- Mainpuri
- Majuli
- Malappuram
- Malda
- Malkangiri
- Malout
- Mammit
- Manakudi
- Manapparai
- Manawar
- Mandi
- Mandi Gobindgarh
- Mandla
- Mandsaur
- Mandya
- Mangalore
- Manipal
- Mannargudi
- Mansa
- Margao
- Marigaon
- Mathura
- Mau
- Mayurbhanj
- Medak
- Meenkashipuram
- Meerut
- Mehsana
- Melaparuthigudi
- Melpallam
- Melpattamkarisalkulam
- Melvisharam
- Midnapore
- Mirzapur
- Moga
- Mohali
- Mohanur
- Mokokchung
- Mon
- Moradabad
- Morena
- Muchipara
- Mughal Sarai
- Muktsar
- Mumbai
- Mumbai Extension
- Munger
- Murshidabad
- Muzaffarnagar
- Muzaffarpur
- Mysore
- Nabarangapur
- Nadia
- Nadiad
- Naduvakurichi
- Nagaon
- Nagapattinam
- Nagaur
- Nagpur
- Naidupuram
- Nainital
- Najibabad
- Nalanda
- Nalbari
- Nalgonda
- Namakkal
- Nanded
- Nandurbar
- Narayanpur
- Narmada
- Narnaulajsbd
- Narsinghpur
- Narsipatnam
- Nashik
- Navi Mumbai
- Navsari
- Nawada
- Nawanshahr
- Naxalbari
- Nayagarh
- Neemrana
- Neemuch
- Neeraj
- Nelamangala
- Nellore
- Nerur
- New Delhi
- New Kk
- Nicobar
- Nilgiri
- Nilgiris
- Nizamabad
- Noida
- North 24 Parganas
- North And Middle Andaman
- North Cachar Hills
- North Dinajpur
- North Goa
- North Sikkim
- North Tripura
- Nowda
- Nuapada
- Nuh
- Nuvem
- Ooty
- Osmanabad
- Pakur
- Palakkad
- Palamalai
- Palamu
- Palani
- Palghar
- Pali
- Pambakovil Shandy
- Pamjis
- Panaji
- Panchkula
- Panchmahal
- Panipat
- Panna
- Panvel - Station
- Papanasam
- Pappankulam
- Pappinaickenpatti
- Papum Pare
- Paradip
- Parbhani
- Pasumpon
- Patan
- Pathanamthitta
- Pathankot
- Patiala
- Patna
- Pauri Garhwal
- Pavitram
- Perambalur
- Peren
- Phalghat
- Phek
- Pilani
- Pilibhit
- Pinnathur
- Pithoragarh
- Pondicherry
- Ponga
- Poonamalle
- Poonch
- Porbandar
- Port Blair
- Prakasam
- Pratapgarh
- Proddatur
- Pudukkottai
- Pulankurichi
- Pulavadi
- Puludipatti
- Pulwama
- Pune
- Pungamuthur
- Purba Bardhaman
- Purbasthali
- Puri
- Purnia
- Puruliya
- Puzhal
- Quilon
- Raebareli
- Raichur
- Raigad Maharashtra
- Raigarh Chattisgarh
- Raikasba
- Raipur
- Raisen
- Rajahmundry
- Rajauri
- Rajgangpur
- Rajgarh
- Rajkot
- Rajnandgaon
- Rajpura
- Rajsamand
- Ramanagar
- Ramanathapuram
- Ramgarh
- Ramjas
- Rampur
- Ranchi
- Rangareddi
- Rangareddy
- Ranipet
- Rash
- Rasho
- Ratlam
- Ratnagiri
- Raurkela
- Rayagada
- Reasi
- Rewa
- Rewari
- Ri Bhoi
- Rishikesh
- Rohtak
- Rohtas
- Roorkee
- Ropar
- Rourkela
- Rudraprayag
- Rudrapur
- Rupnagar
- Rurka Kalan
- S.A.S. Nagar
- Sabarkantha
- Saegama
- Sagar
- Saharanpur
- Saharsa
- Sahibganj
- Saiha
- Salem
- Samastipur
- Sambalpur
- Sambhal
- Sangareddy
- Sangli
- Sangrur
- Sant Kabir Nagar
- Sant Ravidas Nagar
- Saran
- Sare
- Sarega
- Saregamapa
- Satara
- Satna
- Sawai Madhopur
- Secunderabad
- Sehore
- Senapati
- Seoni
- Seraikela-Kharsawan
- Serchhip
- Shahapur
- Shaharanpur
- Shahdol
- Shahjahanpur
- Shahpura
- Shajapur
- Shamshabad
- Sheikhpura
- Sheohar
- Sheopur
- Shikohabad
- Shillong
- Shimla
- Shimoga
- Shivpuri
- Shrawasti
- Shyamnagar
- Sibmandir
- Sibsagar
- Siddharthnagar
- Sidhi
- Sihora
- Sikar
- Siliguri
- Silvassa
- Simdega
- Simga
- Sindhudurg
- Singrauli
- Sirkaali
- Sirmaur
- Sirohi
- Sirsa
- Sitamarhi
- Sitapur
- Sivaganga
- Sivakasi
- Sivasagar
- Siwan
- Solan
- Solapur
- Sonapur
- Sonarpur
- Sonbhadra
- Sonipat
- Sonitpur
- Soro
- South 24 Parganas
- South Andaman
- South Dinajpur
- South Garo Hills
- South Goa
- South Sikkim
- South Tripura
- Sricity
- Srikakulam
- Srinagar
- Subarnapur
- Sujangarh
- Sultanpur
- Sundergarh
- Supaul
- Surat
- Surendranagar
- Surguja
- T Pudupatti
- Tadipatri
- Talasari
- Tamenglong
- Tapi
- Tarn Taran
- Tawang
- Tehri Garhwal
- Tenkasi
- Thane
- Thanjavur
- The Dangs
- Theni
- Thimmarajanpettai
- Thirukkalukundram
- Thirukkannamangaikottam
- Thiruvaiyaru
- Thiruvarur
- Thoothukudi
- Thoubal
- Thrissur
- Thungavi
- Tikamgarh
- Timarni
- Tinsukia
- Tirap
- Tiruchendur
- Tiruchirappalli
- Tiruklalikundram
- Tirumani
- Tirunelveli
- Tirupati
- Tiruppur
- Tirupur
- Tirur
- Tiruttani
- Tiruvalla
- Tiruvallur
- Tiruvannamalai
- Tiruvarur
- Titilagarh
- Tohana
- Tonk
- Trimulgherry
- Trivandrum
- Tuensang
- Tumkur
- Turaiyur Koitpatti
- Tuticorin
- Udaipur Rajasthan
- Udaipur Tripura
- Udayarpalayam
- Udham Singh Nagar
- Udhampur
- Udupi
- Ujjain
- Ukhrul
- Umaria
- Una
- Unnao
- Upper Siang
- Upper Subansiri
- Uttara Kannada
- Uttarkashi
- Vadagarai
- Vadakara
- Vadodara
- Vaishali
- Valsad
- Vandavasi
- Vapi
- Varanasi
- Vattur
- Vellore
- Vidisha
- Vijayawada
- Vikarabad
- Villupuram
- Virudhunagar
- Visakhapatnam
- Visalakshi Nagar
- Vizianagaram
- Warangal
- Wardha
- Washim
- Wayanad
- West Champaran
- West Garo Hills
- West Godavari
- West Kameng
- West Khasi Hills
- West Midnapore
- West Nimar
- West Siang
- West Sikkim
- West Singhbhum
- West Tripura
- Wokha
- Y.S.R.
- Yadgir
- Yamunanagar
- Yavatmal
- Zunhebotto
- BP Monitors
- Masks (N95, Surgical and more)
- Surgical Masks
- Face Shield
- N95 Masks
- N99 Masks
- Nebulizers & Vaporizers
- Oximeters & Pedometers
- Vital Signs Monitors & Wearables
- Oxygen Concentrators & Cans
- Weighing Scales
- Thermometers
- IR Thermometers
- Body Massager
- Diabetes Monitors
- Mobility Equipments
- Exercise Equipments
- Doctor's Corner
- Stethoscopes
- Tapes & Bandages
- Clinical Diagnostic Equipments
- Dressings & Wound Care
- Supports & Braces
- Neck & Shoulder Support
- Knee & Leg Support
- Back & Abdomen Support
- Ankle & Foot Support
- Hand & Wrist Braces
- Arm & Elbow Support
- Cervical Pillows
- Compression support & sleeves
- Heel support
- Vitamins & Supplements
- Multivitamins
- TestUdpTemporary
- Vitamins A-Z
- Mineral Supplements
- banner
- Nutritional Drinks
- Adult Daily Nutrition
- Kids Nutrition (2-15 Yrs)
- For Women
- Health Food & Drinks
- Green Tea & Herbal Tea
- Herbal Juice
- Apple Cider Vinegar
- Healthy Snacks
- Protein Supplements
- Whey Protein
- Amino Acids
- Mass Gainers
- Workout Essential
- Fat Burners
- Ayurveda Top Brands
- Dabur
- Sri Sri Tattva
- Baidyanath Products
- Kerala Ayurveda
- Jiva Ayurveda
- Tata 1mg Herbal Supplements
- Patanjali
- test_udp
- test_udp_1
Want to know more?
Read Our Editorial PolicyHave issue with the content?
Report Problem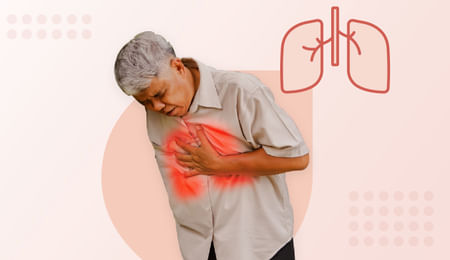
Lung cancer
Also known as Lung carcinoma, Lung tumor, and Cancer of the lungsOverview
Cancer is a medical condition in which the body starts to uncontrollably grow some cells that can also end up spreading to other parts of the body. Lung cancer is a type of cancer that occurs and affects the infected person's lungs. It causes uncontrolled growth of lung tissues and can spread rapidly to other regions such as lymph nodes, brain, adrenal glands, liver, and bones.
The exact cause of lung cancer is still unknown. However, the leading cause of this disease is smoking, and the risk of incurring lung cancer has been associated with prolonged smoking. Quitting smoking has been shown to significantly decrease a person's chance of developing the disease.
In the initial stages, lung cancer does not show any symptoms. Symptoms that appear at an advanced stage usually include a persistent cough that doesn't go away, spotting blood while coughing, shortness of breath, hoarseness, losing weight, chest pain, and headaches.
There are different types of lung cancers, and the treatment for the same depends on the type and stage of the lung cancer. Treatment modalities can include a combination of surgery, chemotherapy, radiotherapy, and immunotherapy.
Key Facts
- Age above 70 years
- Both men and women
- Bronchi
- Lungs
- Lymph nodes
- Heart
- Spine
- Pneumonia
- Asthma
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- Bronchitis
- Pleural effusion
- Pneumothorax
- Tuberculosis
- Acid reflux
- Radiotherapy
- Immunotherapy
- Chemotherapy
- Targeted drug therapy
- Surgery: Wedge resection, Segmental resection & Pneumonectomy
- General physician
- Oncologist
- Pulmonoligist
Symptoms Of Lung Cancer
Like other cancers, the symptoms of lung cancer become more evident in the later stages of the disease than in earlier stages. Patients usually notice these symptoms when the disease advances to the higher stages. A few symptoms seen in lung cancer include the following.
-
A persistent cough that doesn't go away
-
Spotting blood in cough
-
Hoarseness
-
Losing weight for no evident reason
-
Bone pain
-
Trouble in breathing
-
Shortness of breath
-
Chest pain
-
Cough that worsens with time
-
Persistent or recurrent chest infection
-
Trouble during swallowing
-
Wheezing
-
Loss of appetite
-
Fatigue
-
Swelling of the face and veins
-
Finger clubbing
-
Enlargement of lymph nodes in and above the clavicle
-
Thrombocytosis (excessive production of platelets)
Here are some common signs and symptoms that could be suggestive of cancer.
Types Of Lung Cancer
Generally, the most common types of lung cancer are seen in the lungs itself, other rare types of cancer may also occur outside the lungs and chest wall. Types of lung cancer include:
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)
Cases of NSCLC are more commonly seen, and nearly 80%-85% of cases of lung cancer are non-small cell lung cancer. The subtypes of NSCLC are as follows:
1. Adenocarcinoma: This kind of cancer starts in the cells of the lungs that are responsible for secreting a substance called mucus. It is typically seen in smokers or past smokers but is also one of the most common cancers to affect non-smokers. Adenocarcinoma tends to affect women more than men and is likely to affect younger people. This cancer is usually found in the outer regions of the lungs and is typically diagnosed before it has spread to other parts of the body.
2. Squamous cell carcinoma: Squamous cells are flat cells that line the inside of the airways of the lungs. Squamous cell carcinoma starts in squamous cells and is linked with a history of smoking. Doctors tend to find this cancer in the centre of the lungs, typically near the main airway or bronchus.
3. Large cell carcinoma: This kind of cancer tends to appear in any part of the lung and is also known as undifferentiated cancer. Large cell carcinoma grows and spreads rapidly, which can make it harder to treat.
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC)
This kind of cancer is almost exclusively seen in heavy smokers and is found less commonly in non-smokers. Almost 10-15% of cases are SCLC, also referred to as oat cell cancer. This cancer tends to grow and spread faster than the other varieties, and almost 70% of affected people are diagnosed with the disease at a stage where cancer has already spread to other parts of the body. This kind of cancer responds better to treatment modalities such as chemotherapy and radiation therapy. However, the chances of SCLC returning are higher, and the patients are warned about the same.
Other types
1. Mesothelioma: Mesothelioma is a rare cancer of the chest lining, commonly caused by asbestos exposure. It accounts for about 5 percent of all lung cancer cases. Mesothelioma develops over a period of 30 to 50 years between exposure to asbestos and getting cancer.
2. Chest wall tumours: These are rare and can be malignant (cancerous) or benign (non-cancerous). Malignant tumours must be treated. Benign tumours are treated depending on where they are located and the symptoms they cause.
3. Metastatic lung cancer: These kinds of cancers don't start in the lungs and are not lung cancers. Often cancer can start in other parts of the body and spread to the lungs in the later stages, which are called metastatic cancer. Almost any cancer can metastasize to the lung. Some cancers that often spread to the lung are:
-
Bladder cancer
-
Neuroblastoma (cancer of immature nerve cells)
-
Sarcoma
-
Wilms' tumour (kidney cancer in children)
Learn everything about prostate cancer from causes and risk factors to treatment.
Causes Of Lung Cancer
Typically smoking causes lung cancer. First-hand smoking or persistent exposure to second-hand smoke has been the leading cause of lung cancer. However, lung cancer can also develop in patients who aren't smokers and have never been exposed to second-hand smoke. In such cases, there is no clear cause behind the occurrence of lung cancer.
Doctors believe that smoking damages the lining of the lungs and hence causes lung cancer. Cigarette smoke is filled with heavy carcinogens (cancer-causing substances) that start affecting the healthy lining of the lungs. In the initial stages, the body tries its best to repair the damage. However, repeated exposure results in increasing damage to the lining of the lungs and over time, causes the lung cells to sustain permanent damage. This results in the development of cancer.
Risk Factors For Lung Cancer
A risk factor is anything that increases a person’s chance of getting a disease. Risk factors for lung cancan can be classified into the following:
Modifiable risk factors
1. Smoking: The number of cigarettes a person smokes and the number of years they have smoked affect a person's chances of incurring lung cancer. The risk of lung cancer increases if a person is a chronic smoker. It is advisable to quit smoking at any age to reduce the risk of developing lung cancer.
Here’s more on how smoking can affect your lungs.
2. Secondhand smoke: Getting exposed to second-hand smoke also increases a person’s risk of developing lung cancer.
3. Exposure to radon gas: These exposures can occur if you live in an area with a high level of radon, an element made by the breakdown of uranium in the soil, water, and rock. This radon becomes a part of the air you breathe and can accumulate to unsafe levels. According to the US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), radon is the second leading cause of lung cancer in the US and is the leading cause among people who don't smoke.
4. Exposure to asbestos: Getting exposed in workplaces to elements such as asbestos can cause lung cancer and increase a person's chances of developing the disease. This risk is especially high in smokers. People exposed to large amounts of asbestos also have a greater risk of developing mesothelioma, a type of cancer that starts in the pleura (the lining surrounding the lungs).
5. Exposure at the workplace: Other carcinogens (agents that can cause cancer) found in some workplaces can increase the risk of developing lung cancer. They include:
-
Radioactive ores such as uranium
-
Inhaled chemicals such as arsenic, beryllium, cadmium, silica, vinyl chloride, nickel compounds, chromium compounds, coal products, mustard gas, and chloromethyl ethers
-
Diesel exhaust
6. Diet: Studies have suggested that diet is responsible for approximately 30% of all cancers. Many reports suggest that dietary factors contribute to the risk for lung cancers. For example, low serum concentrations of antioxidants, such as vitamins A, C, and E, have been associated with the development of lung cancer.
Non-modifiable risk factors
1. Family history: If you have a family history of lung cancer, the chances of you incurring the same can increase exponentially. Talk to your family about any history of lung cancer in the family.
2. Previous history of lung diseases: Chronic inflammatory lung diseases such as asthma, chronic obstructive lung disorder (COPD), and tuberculosis, are associated with an increased lung cancer risk in later life.
Note: Patients with early-stage lung cancer are often misdiagnosed as tuberculosis due to the common symptoms which leads to a delay in the correct diagnosis. One should not go for antitubercular medication unless relevant investigations have been performed to rule out lung cancer.
Read more about tuberculosis.
3. Air pollution: In cities, with heavily trafficked roads, air pollution (especially near) appears to raise the risk of lung cancer slightly.
4. Gender: Smoking prevalence is higher among men than women which is the leading cause of lung cancer.
Diagnosis Of Lung Cancer
If your doctor suspects lung cancer, they will advise a series of tests to confirm the diagnosis.
Imaging tests
Imaging modalities such as an X-ray, CT scan, an MRI, or PET scan are advised by healthcare professionals to view the areas of lung tissues that can be affected by cancer.
A positron emission tomography (PET scan) is an imaging test that utilizes radiation to reveal the activity of cells within the body. It helps healthcare professionals to diagnose health conditions and the effectiveness of treatment plans. The PET scan reveals multidimensional colour images of the workings of the body and displays how the organ looks while also telling doctors about their functioning. A healthcare professional will inject a radiotracer (a radioactive material tagged to a natural chemical such as glucose) into the body, and the machine will detect the radiation released by the radiotracer. The areas of the body that need more energy are called the ‘hot spot’ and are seen bright on the PET scan. These hot spots indicate cancer cells since these cells are very active and use glucose more rapidly.
Tissue samples
A doctor may wish to test your tissues to check for cancer cells and send a sample of the affected tissue for a biopsy to the laboratory. This process is carried out using a fine needle aspiration biopsy (FNAC) or a bronchoscope. A bronchoscope is a device that has a thin, lighted end with a camera attached to its end. The device enters the mouth or nose, where a healthcare professional can view the organs through the camera on a screen and look for lesions. The scope will allow the doctors to take a sample from the lesions and send them for further diagnosis. Some less accessible areas may require more invasive surgeries, such as a thoracoscopy to remove lung tissue for a sample.
Prevention Of Lung Cancer
There is no certain way through which one can prevent lung cancer. However, there are certain steps that a person can take to reduce their risk of getting lung cancer.
Stop smoking
Smokers have shown to be at a higher risk of incurring lung cancer. If you have never smoked, stick to that and avoid smoking for any reason. If you are a smoker, quit smoking. Quitting at any stage of your life significantly reduces the risk of developing lung cancer. Talk to your family and healthcare professionals who specialise in helping people quit smoking.
Several clinics have tobacco cessation sessions that help people in quitting an addiction. You can also attend meetings and support groups where like-minded people gather to talk about their journey of quitting the said addiction. One can also opt for nicotine patches and other medications to help one quit smoking.
Want To Quit Smoking? 7 Practical Ways To Do So!
Avoid second-hand smoke
If you live in an area or with a family member who is a frequent smoker, encourage them to quit or like them to smoke outside. Getting frequently exposed to second-hand smoke can also increase a person's risk of developing lung cancer. Avoid visiting places where people would be smoking in closed confines such as bars and pubs.
Secondhand smoke is as dangerous as active smoking. Here are 20 common smoking myths busted!
Test your home for radon
Contact your municipality officers for the methods through which you can test your home for radon levels. If you live in an area where the radon is a known problem, contact the local department to learn about how you can minimise your risk and take remedies to make your home a safer place for you and your family.
Avoid carcinogens
If you are employed in work fields that require you to follow certain safety protocols to avoid exposure to carcinogens such as asbestos, follow those precautions. Take advice from your doctor on ways through which you can protect yourself from carcinogens at work. If you are a frequent smoker, your risk of developing lung cancer from exposure to carcinogens at work increases to quite some extent. Take precautions to avoid getting exposed to toxic chemicals at your workplace.
Eat a healthy diet
Take a healthy diet that is rich in fruits and vegetables. Choose food sources that have a high nutrient value. Consult your doctor before taking vitamins in supplements form since some supplements can increase the risk of lung cancer. Vitamin A and its family of compounds (the retinoids) have shown to have chemopreventive properties.
Here are 5 superfoods that fight cancer and gift you healthy life.
Try chemoprevention
Chemoprevention is defined as the use of agents to prevent, inhibit, or reverse the process of carcinogenesis.
Understand the biomarkers of cancer
A better understanding of the molecular events that occur during carcinogenesis has opened new areas of research in cancer prevention. Currently, pre-neoplasia is diagnosed based on histological examinations.
Lower exposure to workplace risk factors
Exposure to certain chemicals at the workplace have shown to increase the risk of lung cancer. Taking precautionary measures to avoid the exposure can be beneficial in the long run.
Exercise regularly
Exercising regularly or at least three days a week can promote a healthier lifestyle. Walking for at least 30 minutes a day is undoubtedly beneficial for overall health. It not only boosts your mood, and aids in weight loss but also improves your heart health, helps relieve stress, and increases your life expectancy.
Walking may improve the quality of life for people with advanced cancer. Click here to read more!
Specialist To Visit
You should visit a doctor if you are experiencing symptoms such as loss of breath, difficulty in breathing, persistent coughing, blood in cough or sputum, fatigue, back pain, headache, wheezing, and pain in the chest. These symptoms might indicate the possibility of a medical condition behind the symptoms.
You can consult the following doctors for diagnosis:
-
General physician
-
Oncologist
-
Pulmonologist
A pulmonologist diagnoses and treats diseases of the respiratory system. An oncologist is a medical practitioner qualified to diagnose and treat tumours.
Consult India's best doctors online with a single click. Book an appointment now!
Treatment Of Lung Cancer
Cancer is treated depending on the stage and extent of your cancer. The staging of cancer will help your healthcare professional decide the treatment modalities that will work the best for you. Your doctor will carry out some staging tests to determine the extent of your cancer. These tests will include the various diagnostic procedures mentioned above such as PET scan, CT, and MRI. The lowest stage of cancer indicates that the cancer is restricted to the lung. Higher stages indicate the spread of cancer, in which stage IV is considered an advanced stage and indicates that the disease has spread to other parts of the body other than the lungs.
Depending on your health and the stage of your cancer, your doctor will decide your treatment plan. Some people may not choose to undergo the treatment since they might feel that the risks of the treatment outweigh the benefits. Elderly people in advanced stages may feel this way; hence it is important to talk to your doctor about the various treatment plans and the potential risks they carry. Treatment options for cancer include:
Surgery
A surgical procedure may be carried out to remove the affected area along with a healthy margin of the tissue. These procedures include:
-
Wedge resection: In this, a small section of the lung is removed to resect the cancer cells along with a margin of healthy tissue.
-
Segmental resection: This allows a doctor to remove a larger area of the lung, whereas a lobectomy involves removing the entire affected lobe of the lung.
-
Pneumonectomy: This procedure involves the removal of an entire lung.
In the advanced stages of cancer, the lymph nodes may also get affected. In such cases, the surgeon may remove some lymph nodes to check for the signs of the spread of cancer. If your cancer is confined to the lungs, your surgeon may suggest surgery. However, large areas may require chemotherapy or radiotherapy before the surgery to reduce the size of the tumour. Sometimes, doctors may recommend radiotherapy or chemotherapy after a surgical process to ensure that all cancer cells are dead.
Radiation therapy
This is a treatment modality that uses high-powered energy beams that work as an effective treatment to kill cancer cells. During a radiation therapy appointment, the patient is asked to lie flat on a table. A large machine that emits the energy beam moves around the body and aims the beam at precise points. Radiation therapy is often recommended for patients who have localised lung cancer and can also be recommended after surgery to remove the affected tissue.
Radiation therapy can lead to some side effects including nausea and fatigue. It can also cause some level of skin erythema (redness) and irritation near the abdominal and groin areas. Before the radiation therapy, you can talk to your doctor about the side effects and methods of managing the same. Several men opt to preserve their sperm before beginning radiation therapy.
Stereotactic body radiotherapy
Radiotherapy, also known as stereotactic body radiotherapy, is an intense form of radiation treatment in which the cancer is subjected to several beams of radiation from different angles. Radiotherapy is usually done over one or few appointments and is considered a good option for people with small lung cancers that haven't spread to other parts of the body or for small cancers in sites that aren't accessible easily. It can also be used to treat cancer that has spread to other parts of the body.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy treatment is a treatment modality that uses strong medicines that are effective in killing cancer cells. These drugs circulate around the body and aim at destroying cancer cells that may have travelled from the original tumour. According to stage 0 lung cancer, chemotherapy may be your only treatment option, or a patient can be advised chemotherapy prior to or post a lymph node surgery. It can be advised alone or along with radiotherapy. Patients are given a combination of medications over a period of months or weeks where the medicines travel in the body via a vein or are given orally. Chemotherapy also helps in reducing the size of the tumours hence making it easier for surgeons to remove the mass completely.
Targeted drug therapy
This kind of treatment focuses on specific abnormalities that may be present within the cancer cells. These drugs block the abnormalities and hence can cause the cancer cells to die. Targeted drug therapy is often considered a treatment option for people with recurrent cancer or advanced cancer, and some targeted therapies work specifically in patients whose cancer cells have specific genetic mutations. Before undergoing targeted therapy, your cancer cells may be sent for testing in laboratories to check which drug is right for you.
Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy takes the help of the body’s own immune system to help in fighting cancer. Generally, the immune system helps in fighting foreign bodies such as cancer cells, however, sometimes, the immune system stops attacking the cancer cells because they start producing proteins that help the cancer cells in hiding from the immune system. Immunotherapy helps by interfering with that process and helps the immune system in identifying the cancer cells and lets it destroy them. This treatment modality is advised for people with advanced lung cancers and cancers that have metastasized (spread) to other parts of the body.
Home-care For Lung Cancer
Learning that one has cancer can be scary and cause people to panic. However, modern science has allowed several options to open up and the prognosis to look better than ever before. Getting diagnosed with cancer can be overwhelming; hence it is important to cope with the distress of the same and focus on your treatment with the help of your family and loved ones.
-
If you have been prescribed medications to manage your medical condition, make sure you take those medications on time.
-
Label your drugs and set the alarm to make sure you have the medicines every day at the same time. Follow all the instructions given to you by your doctor.
-
Follow the diet given to you by your doctor.
-
Ask your doctor about your diagnosis and the different treatment options available for you. Learning about cancer and having an idea about what's to come in the next few months can help you cope with the uncertainty of cancer. Learning about cancer can also help you in making the right choice regarding your treatment.
-
It is important to talk to your family and loved ones during the course of your treatment. Cancer treatments can be isolating and scary, and patients often require practical support to help them through the treatment.
-
You can opt for counsellors or support groups where people going through similar experiences gather to talk about their experiences with the disease. The shared concern and understanding can help you deal with the outcome of cancer.
Complications Of Lung Cancer
Progressive lung cancer can cause several complications down the road. This can be caused due to the spread of cancer to different parts of the body or as a result of certain cancer treatments.
Superior vena cava syndrome
The presence of tumors in the upper area of the right lung can prevent blood from flowing through the superior vena cava, a large vein that is responsible for carrying blood from the upper body towards the heart. This results in superior vena cava syndrome and is associated with loss of consciousness, dizziness and facial swelling.
Metastasis
Over time, cancer can spread to other parts of the body, such as the brain, adrenal glands, and bones. In some cases, cancer is detected after cancer has spread to other parts of the body from the original site and is commonly seen in advanced stages of cancer.
Lung infections
Patients with lung cancer are more prone to getting affected with infections such as bronchitis or pneumonia since the immune system has decreased activity due to cancer itself or as a result of cancer treatments.
Heart blockage
Sometimes, cancer can spread to the heart and result in compression of the veins and the arteries. This can result in the buildup of fluids and heart blockage along with arrhythmias or heart attacks.
Hypercalcemia
Hypercalcemia is a condition in which the body has high levels of calcium that can lead to vomiting, excessive thirst, and stomach pain.
Blood clots
People with lung cancer are at a higher risk of developing blood clots and deep vein thrombosis, which results from the formation of a blood clot in a deep vein. If the blood clot travels to the lungs, it can prevent the blood flow and result in a fatal condition called pulmonary embolism.
Neuropathy
Tumours present in the top of the lungs can affect the eyes, face and shoulders which can cause arm and shoulder pain. It can also result in Horner's syndrome, in which the patient experiences droopy eyelids and changes in the size of the pupil.
Spinal cord compression
Some patients may start experiencing constant back pain that can be due to the spread of cancer to the spine. This causes compression of the vertebrates (spinal bones), resulting in weakness and back pain. Around 28% of people with lung cancer may experience this condition.
In India, only 15-20% of lung cancer cases are detected in the early stages. Read about things you should know about lung cancer.
Alternative Therapies For Lung Cancer
Lung cancer requires orthodox medical treatment. However, some patients feel that a complementary approach via alternative therapies can help in the management of the side effects caused during the treatment. These consist of:
Acupuncture
Acupuncture has proven to be a successful alternative therapy form for patients that have lung cancer. But provide relief for patients and also ease symptoms such as nausea and vomiting, which are common side effects of cancer treatments. Acupuncture involves the insertion of needles through the skin at specific points on the body.
Aromatherapy
It uses a mix of essential oils for massages that can make a person feel relaxed. Often patients feel that alternative therapies such as aromatherapy help them cope with the treatment of cancer and allow them to feel relaxed.
Hypnosis
Hypnosis is carried out by a therapist who will help you through certain relaxation exercises that can encourage positive and relaxing thoughts. It also helps in reducing nausea and anxiety seen in people with cancer.
Meditation
It can help you centre your thoughts and promote the feeling of calmness and acceptance. Meditation is said to improve the quality of life and improve a person's mental state.
Practising meditation for just 10-15 minutes a day can go a long way in protecting you against diseases or helping manage them better. Read about 6 ways how meditation can improve your life.
Living With Lung Cancer
Being diagnosed with lung cancer can cause stress and anxiety in patients. This medical condition directly affects the quality of life, and patients struggle with the concept of cancer itself. Cancer affects your day-to-day life and also affects the following months of your life. Here are a few things to keep in mind.
Take care of yourself
Preparing for the treatment of lung cancer can seem like a daunting task. To do so, you need to take care of yourself and your body. Eat a healthy diet that is well balanced. Increase the number of fruits and vegetables you intake and get plenty of rest every night. Try to practice meditation and eliminate sources of stress from your life prior to the treatment. Talk to your doctor about strategies that can help your body prepare for the treatment.
Try to relax
Patients with lung cancer can often feel short of breath, and fear and anxiety makes it even harder. Learn to identify these instances, and the next time you start feeling short of breath, focus on managing the fear by opting for an activity such as meditation to help you reduce your anxiety and help you relax. Focus on moving the muscles of your diaphragm instead of trying to fill your lungs with air and breathing with pursed lips while pacing your breathing.
Save your energy
Cancer often causes fatigue and makes a person feel tired during the course of the treatment. Cut down on non-essential tasks and enlist the support of your family members that can help you in carrying out day-to-day tasks.
Cope with emotions
Living with lung cancer can bring up emotions. To keep yourself emotionally healthy during your journey, talk to your friends and family, talk to other people in the same situation, know about your condition, do not try to do too much, and make time for yourself.
Get help from support groups
The lung cancer community is growing. Many people have been touched by lung cancer. There are lots of active support groups for patients and family caregivers, so no one has to face a lung cancer diagnosis alone.
References
- Bradley SH, Kennedy MPT, Neal RD. Recognising Lung Cancer in Primary Care [published correction appears in Adv Ther. 2020 Apr.
- Risk factors. Lung Cancer Causes, Risk Factors, and Prevention. American Cancer Society. Oct 2019.
- Lung Cancer: Epidemiology, Aetiology, and Prevention. Charles S. Dela Cruz, MD, PhDa,*Lynn T. Tanoue.Clin Chest Med. 2011 December.
- Non-small cell lung cancer. National Comprehensive Cancer Network. Jan 2020.
- Niederhuber JE, et al., eds. Cancer of the lung: Non-small cell lung cancer and small cell lung cancer. In: Abeloff's Clinical Oncology. 6th ed. Elsevier; Jan 2020.
- National Cancer Institute. Physician Data Query (PDQ). Health Professional Version. Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Treatment. Jun 2019.
- Lung cancer prevention (PDQ). National Cancer Institute. Mar 2020.
- Lung cancer — non-small cell: Screening. American Society of Clinical Oncology. Mar 2020.