- TOP CITIES
- New Delhi
- Gurgaon
- Pune
- Mumbai
- Bengaluru
- Kolkata
- Hyderabad
- Ahmedabad
- Chennai
- Indore
- Lucknow
- Jaipur
- Chandigarh
- Bhopal
- Noida
- Navi Mumbai
- Surat
- Patna
- Ludhiana
- Bhubaneshwar
- ALL CITIES
- Abohar
- Adad
- Adilabad
- Adoni
- Adsaidnakda
- Agar
- Agartala
- Agra
- Ahmedabad
- Ahmednagar
- Aizawl
- Ajmer
- Akola
- Aksjdhbaskjda
- Alappuzha
- Aligarh
- Alipurduar
- Alirajpur
- Allahabad
- Almora
- Alwar
- Ambala
- Ambattur
- Ambedkar Nagar
- Amravati
- Amreli
- Amritsar
- Amroha
- Anand
- Anantapur
- Ananthnag
- Anantnag
- Angamally
- Angul
- Ankleshwar
- Annur
- Anuppur
- Arakkonam
- Arambag
- Arantangi
- Araria
- Arcot
- Ariyalur
- Arwal
- Asansol
- Asdbakda
- Ashok Nagar
- Assaudh
- Attuvampatti
- Auraiya
- Aurangabad Bihar
- Aurangabad Maharashtra
- Aviyur
- Ayyangarkulam
- Azamgarh
- Badlapur
- Bagalkot
- Bageshwar
- Baghpat
- Bagpat
- Bahadurgarh
- Bahraich
- Baksa
- Balaghat
- Balangir
- Baleswar
- Ballia
- Bally
- Balrampur
- Banaskantha
- Banda
- Bangalore
- Bangalore Rural
- Banka
- Bankura
- Banswara
- Barabanki
- Baramati
- Baramulla
- Baran
- Baraut
- Bardhaman
- Bareilly
- Bargarh
- Barmer
- Barnala
- Barpeta
- Barrackpore
- Baruipur
- Barwani
- Basirhat
- Bastar
- Basti
- Bathinda
- Beawar
- Beed
- Begumganj
- Begusarai
- Behraghora
- Behrampur
- Belgaum
- Bellary
- Belur
- Bengaluru
- Betul
- Betul Ganj
- Bhadrak
- Bhadravati Karnataka
- Bhagalpur
- Bhandara
- Bharatpur
- Bharuch
- Bhatkal
- Bhavani
- Bhavnagar
- Bhilai
- Bhilwara
- Bhind
- Bhiwadi
- Bhiwandi
- Bhiwani
- Bhojpur
- Bhopal
- Bhubaneshwar
- Bhuna
- Bhusawal
- Bidar
- Bijapur Chattisgarh
- Bijapur Karnataka
- Bijnor
- Bikaner
- Bilaspur Chattisgarh
- Bilaspur Himachal Pradesh
- Birbhum
- Bishnupur
- Boisar
- Bokaro
- Bongaigaon
- Bongaon
- Botad
- Boudh
- Budaun
- Budgam
- Bukkapatnam
- Bulandshahr
- Buldana
- Buldhana
- Bundi
- Burdwan
- Burhanpur
- Buxar
- Cachar
- Calicut
- Chamarajanagar
- Chamba
- Chamoli
- Champawat
- Champhai
- Chandauli
- Chandel
- Chandigarh
- Chandrapur
- Changanassery
- Changlang
- Chatra
- Chennai
- Chhatarpur
- Chhindwara
- Chikkaballapur
- Chikkaballapura
- Chikmagalur
- Chintamani
- Chitradurga
- Chitrakoot
- Chittoor
- Chittorgarh
- Chrompet
- Churachandpur
- Churu
- Cochin
- Coimbatore
- Cooch Behar
- Cuddalore
- Cuddapah
- Cuttack
- Dadra & Nagar Haveli
- Dahanu
- Dahod
- Dakshina Kannada
- Daman
- Damoh
- Dans
- Dantewada
- Darbhanga
- Darjiling
- Darrang
- Datia
- Dausa
- Davangere
- Debagarh
- Dehradun
- Delhi
- Deoghar
- Deoria
- Dera Bassi
- Devanahalli
- Dewas
- Dhakaoli
- Dhalai
- Dhamtari
- Dhanbad
- Dhar
- Dharmapuri
- Dharwad
- Dhemaji
- Dhenkanal
- Dholpur
- Dhone
- Dhubri
- Dhule
- Dhully
- Dibang Valley
- Dibrugarh
- Dibrugarh Tamil Nadu
- Dimapur
- Dindigul
- Dindori
- Dispur
- Diu
- Doda
- Dombivli
- Dombivli Station
- Dumka
- Dungarpur
- Durg
- Durgapur
- East Champaran
- East Garo Hills
- East Godavari
- East Kameng
- East Khasi Hills
- East Midnapore
- East Nimar
- East Siang
- East Sikkim
- East Singhbhum
- Ellanaickenpatti
- Ernakulam
- Erode
- Etah
- Etawah
- Faizabad
- Faridabad
- Faridkot
- Farrukhabad
- Fatehabad
- Fatehgarh Sahib
- Fatehpur
- Fazilka
- Fewf
- Fewp
- Firozabad
- Firozpur
- Gadag
- Gadarwara
- Gadchiroli
- Gajapati
- Gandhinagar
- Ganganagar
- Gangtok
- Ganjam
- Garhwa
- Gariaband
- Gautam Buddha Nagar
- Gaya
- Ghaziabad
- Ghazipur
- Gir Somnath
- Giridh
- Goa
- Goalpara
- Gobichettipalayam
- Godda
- Golaghat
- Golaniya
- Gonda
- Gondia
- Gopalganj
- Gopalmath
- Gorakhpur
- Greater Noida
- Greater Thane
- Gulbarga
- Gumla
- Guna
- Guntur
- Gurdaspur
- Gurgaon
- Guwahati
- Gwalior
- Hailakandi
- Halol
- Hamirpur Himachal Pradesh
- Hamirpur Uttar Pradesh
- Hansi
- Hanumangarh
- Hapur
- Harapanahalli
- Harda
- Hardoi
- Haridwar
- Hassan
- Hathras
- Haveri
- Hazaribag
- Hazaribagh
- Hdhd
- Hinauti
- Hindaun
- Hingoli
- Hisar
- Hojai
- Hooghly
- Hosakote
- Hoshangabad
- Hoshiarpur
- Hoskote
- Hospet
- Hosur
- Howrah
- Hubli
- Hyderabad
- Ichalkaranji
- Idukki
- Imphal
- Imphal East
- Imphal West
- Indore
- Itanagar
- Jabalpur
- Jagatsinghapur
- Jaintia Hills
- Jaipur
- Jaisalmer
- Jajapur
- Jalandhar
- Jalaun
- Jalgaon
- Jallipatti
- Jalna
- Jalore
- Jalpaiguri
- Jammu
- Jamnagar
- Jamshedpur
- Jamtara
- Jamui
- Janjgir-Champa
- Jashpur
- Jaunpur
- Jayamala
- Jehanabad
- Jhabua
- Jhai
- Jhajjar
- Jhalawar
- Jhansi
- Jhargram
- Jharsuguda
- Jhujhunu
- Jind
- Jodhpur
- Jorhat
- Junagadh
- Jyotiba Phule Nagar
- Kachchh
- Kadamakkudy
- Kadapa
- Kadiri
- Kadthal
- Kaghaz Nagar
- Kaimur Bhabua
- Kaithal
- Kakinada
- Kalahandi
- Kalipahari
- Kallakurichi
- Kalligudi
- Kalyani
- Kamal
- Kamrup
- Kanadukathan
- Kanchipuram
- Kandhamal
- Kandukur
- Kangra
- Kanker
- Kannauj
- Kannur
- Kanpur
- Kanpur Dehat
- Kanpur Nagar
- Kansapuram
- Kanyakumari
- Kapurthala
- Kar
- Karad
- Karaikal
- Karaikudi
- Karatholuvu
- Karauli
- Karbi Anglong
- Kargil
- Karimganj
- Karimnagar
- Karnal
- Karupatti
- Karur
- Karwar
- Kasaragod
- Kathua
- Katihar
- Katni
- Kattupakkam
- Kaushambi
- Kavaratti
- Kawardha
- Kendrapara
- Kendujhar
- Khagaria
- Khammam
- Khandwa
- Khanna
- Kharagpur
- Khargone
- Kheda
- Kheri
- Khorda
- Kichha
- Kinnaur
- Kiphire
- Kishanganj
- Kochi
- Kodagu
- Kodaikanal Observatory
- Koderma
- Kohima
- Kokrajhar
- Kolar
- Kolasib
- Kolhapur
- Kolkat
- Kolkata
- Kollam
- Kooram
- Koppal
- Koraput
- Korba
- Koriya
- Kota
- Kothakudi
- Kothur
- Kottayam
- Kovilpatti
- Koyilandy
- Kozhikode
- Krishna
- Krishnagiri
- Kulgam
- Kullu
- Kumbakonam
- Kumburvayal
- Kundli
- Kupwara
- Kurnool
- Kurukkalpatti
- Kurukshetra
- Kurung Kumey
- Kushinagar
- Kutch
- Laddivadi
- Lahul & Spiti
- Lakhimpur
- Lakhisarai
- Lakshadweep
- Lalitpur
- Lambakheda
- Latehar
- Latur
- Lawngtlai
- Leh
- Lohardaga
- Lohit
- Lonavala
- Longleng
- Lower Dibang Valley
- Lower Subansiri
- Lucknow
- Ludhiana
- Lunglei
- Machur
- Madhepura
- Madhubani
- Madhupur
- Madikeri
- Madurai
- Mahabubabad
- Mahabubnagar
- Mahadanapuram
- Maharajganj
- Mahasamund
- Mahbub Nagar
- Mahe
- Mahendragarh
- Mahoba
- Mainaguri
- Mainpuri
- Majuli
- Malappuram
- Malda
- Malkangiri
- Malout
- Mammit
- Manakudi
- Manapparai
- Manawar
- Mandi
- Mandi Gobindgarh
- Mandla
- Mandsaur
- Mandya
- Mangalore
- Manipal
- Mannargudi
- Mansa
- Margao
- Marigaon
- Mathura
- Mau
- Mayurbhanj
- Medak
- Meenkashipuram
- Meerut
- Mehsana
- Melaparuthigudi
- Melpallam
- Melpattamkarisalkulam
- Melvisharam
- Midnapore
- Mirzapur
- Moga
- Mohali
- Mohanur
- Mokokchung
- Mon
- Moradabad
- Morena
- Muchipara
- Mughal Sarai
- Muktsar
- Mumbai
- Mumbai Extension
- Munger
- Murshidabad
- Muzaffarnagar
- Muzaffarpur
- Mysore
- Nabarangapur
- Nadia
- Nadiad
- Naduvakurichi
- Nagaon
- Nagapattinam
- Nagaur
- Nagpur
- Naidupuram
- Nainital
- Najibabad
- Nalanda
- Nalbari
- Nalgonda
- Namakkal
- Nanded
- Nandurbar
- Narayanpur
- Narmada
- Narnaulajsbd
- Narsinghpur
- Narsipatnam
- Nashik
- Navi Mumbai
- Navsari
- Nawada
- Nawanshahr
- Naxalbari
- Nayagarh
- Neemrana
- Neemuch
- Neeraj
- Nelamangala
- Nellore
- Nerur
- New Delhi
- New Kk
- Nicobar
- Nilgiri
- Nilgiris
- Nizamabad
- Noida
- North 24 Parganas
- North And Middle Andaman
- North Cachar Hills
- North Dinajpur
- North Goa
- North Sikkim
- North Tripura
- Nowda
- Nuapada
- Nuh
- Nuvem
- Ooty
- Osmanabad
- Pakur
- Palakkad
- Palamalai
- Palamu
- Palani
- Palghar
- Pali
- Pambakovil Shandy
- Pamjis
- Panaji
- Panchkula
- Panchmahal
- Panipat
- Panna
- Panvel - Station
- Papanasam
- Pappankulam
- Pappinaickenpatti
- Papum Pare
- Paradip
- Parbhani
- Pasumpon
- Patan
- Pathanamthitta
- Pathankot
- Patiala
- Patna
- Pauri Garhwal
- Pavitram
- Perambalur
- Peren
- Phalghat
- Phek
- Pilani
- Pilibhit
- Pinnathur
- Pithoragarh
- Pondicherry
- Ponga
- Poonamalle
- Poonch
- Porbandar
- Port Blair
- Prakasam
- Pratapgarh
- Proddatur
- Pudukkottai
- Pulankurichi
- Pulavadi
- Puludipatti
- Pulwama
- Pune
- Pungamuthur
- Purba Bardhaman
- Purbasthali
- Puri
- Purnia
- Puruliya
- Puzhal
- Quilon
- Raebareli
- Raichur
- Raigad Maharashtra
- Raigarh Chattisgarh
- Raikasba
- Raipur
- Raisen
- Rajahmundry
- Rajauri
- Rajgangpur
- Rajgarh
- Rajkot
- Rajnandgaon
- Rajpura
- Rajsamand
- Ramanagar
- Ramanathapuram
- Ramgarh
- Ramjas
- Rampur
- Ranchi
- Rangareddi
- Rangareddy
- Ranipet
- Rash
- Rasho
- Ratlam
- Ratnagiri
- Raurkela
- Rayagada
- Reasi
- Rewa
- Rewari
- Ri Bhoi
- Rishikesh
- Rohtak
- Rohtas
- Roorkee
- Ropar
- Rourkela
- Rudraprayag
- Rudrapur
- Rupnagar
- Rurka Kalan
- S.A.S. Nagar
- Sabarkantha
- Saegama
- Sagar
- Saharanpur
- Saharsa
- Sahibganj
- Saiha
- Salem
- Samastipur
- Sambalpur
- Sambhal
- Sangareddy
- Sangli
- Sangrur
- Sant Kabir Nagar
- Sant Ravidas Nagar
- Saran
- Sare
- Sarega
- Saregamapa
- Satara
- Satna
- Sawai Madhopur
- Secunderabad
- Sehore
- Senapati
- Seoni
- Seraikela-Kharsawan
- Serchhip
- Shahapur
- Shaharanpur
- Shahdol
- Shahjahanpur
- Shahpura
- Shajapur
- Shamshabad
- Sheikhpura
- Sheohar
- Sheopur
- Shikohabad
- Shillong
- Shimla
- Shimoga
- Shivpuri
- Shrawasti
- Shyamnagar
- Sibmandir
- Sibsagar
- Siddharthnagar
- Sidhi
- Sihora
- Sikar
- Siliguri
- Silvassa
- Simdega
- Simga
- Sindhudurg
- Singrauli
- Sirkaali
- Sirmaur
- Sirohi
- Sirsa
- Sitamarhi
- Sitapur
- Sivaganga
- Sivakasi
- Sivasagar
- Siwan
- Solan
- Solapur
- Sonapur
- Sonarpur
- Sonbhadra
- Sonipat
- Sonitpur
- Soro
- South 24 Parganas
- South Andaman
- South Dinajpur
- South Garo Hills
- South Goa
- South Sikkim
- South Tripura
- Sricity
- Srikakulam
- Srinagar
- Subarnapur
- Sujangarh
- Sultanpur
- Sundergarh
- Supaul
- Surat
- Surendranagar
- Surguja
- T Pudupatti
- Tadipatri
- Talasari
- Tamenglong
- Tapi
- Tarn Taran
- Tawang
- Tehri Garhwal
- Tenkasi
- Thane
- Thanjavur
- The Dangs
- Theni
- Thimmarajanpettai
- Thirukkalukundram
- Thirukkannamangaikottam
- Thiruvaiyaru
- Thiruvarur
- Thoothukudi
- Thoubal
- Thrissur
- Thungavi
- Tikamgarh
- Timarni
- Tinsukia
- Tirap
- Tiruchendur
- Tiruchirappalli
- Tiruklalikundram
- Tirumani
- Tirunelveli
- Tirupati
- Tiruppur
- Tirupur
- Tirur
- Tiruttani
- Tiruvalla
- Tiruvallur
- Tiruvannamalai
- Tiruvarur
- Titilagarh
- Tohana
- Tonk
- Trimulgherry
- Trivandrum
- Tuensang
- Tumkur
- Turaiyur Koitpatti
- Tuticorin
- Udaipur Rajasthan
- Udaipur Tripura
- Udayarpalayam
- Udham Singh Nagar
- Udhampur
- Udupi
- Ujjain
- Ukhrul
- Umaria
- Una
- Unnao
- Upper Siang
- Upper Subansiri
- Uttara Kannada
- Uttarkashi
- Vadagarai
- Vadakara
- Vadodara
- Vaishali
- Valsad
- Vandavasi
- Vapi
- Varanasi
- Vattur
- Vellore
- Vidisha
- Vijayawada
- Vikarabad
- Villupuram
- Virudhunagar
- Visakhapatnam
- Visalakshi Nagar
- Vizianagaram
- Warangal
- Wardha
- Washim
- Wayanad
- West Champaran
- West Garo Hills
- West Godavari
- West Kameng
- West Khasi Hills
- West Midnapore
- West Nimar
- West Siang
- West Sikkim
- West Singhbhum
- West Tripura
- Wokha
- Y.S.R.
- Yadgir
- Yamunanagar
- Yavatmal
- Zunhebotto
- BP Monitors
- Masks (N95, Surgical and more)
- Surgical Masks
- Face Shield
- N95 Masks
- N99 Masks
- Nebulizers & Vaporizers
- Oximeters & Pedometers
- Vital Signs Monitors & Wearables
- Oxygen Concentrators & Cans
- Weighing Scales
- Thermometers
- IR Thermometers
- Body Massager
- Diabetes Monitors
- Mobility Equipments
- Exercise Equipments
- Doctor's Corner
- Stethoscopes
- Tapes & Bandages
- Clinical Diagnostic Equipments
- Dressings & Wound Care
- Supports & Braces
- Neck & Shoulder Support
- Knee & Leg Support
- Back & Abdomen Support
- Ankle & Foot Support
- Hand & Wrist Braces
- Arm & Elbow Support
- Cervical Pillows
- Compression support & sleeves
- Heel support
- Vitamins & Supplements
- Multivitamins
- TestUdpTemporary
- Vitamins A-Z
- Mineral Supplements
- banner
- Nutritional Drinks
- Adult Daily Nutrition
- Kids Nutrition (2-15 Yrs)
- For Women
- Health Food & Drinks
- Green Tea & Herbal Tea
- Herbal Juice
- Apple Cider Vinegar
- Healthy Snacks
- Protein Supplements
- Whey Protein
- Amino Acids
- Mass Gainers
- Workout Essential
- Fat Burners
- Ayurveda Top Brands
- Dabur
- Sri Sri Tattva
- Baidyanath Products
- Kerala Ayurveda
- Jiva Ayurveda
- Tata 1mg Herbal Supplements
- Patanjali
- test_udp
- test_udp_1
Want to know more?
Read Our Editorial PolicyHave issue with the content?
Report Problem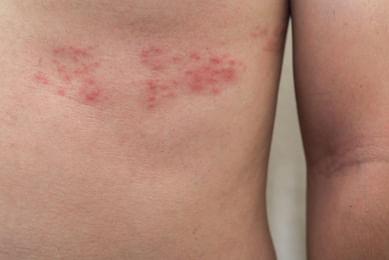
Shingles
Also known as Herpes zosterOverview
Shingles, caused by the varicella-zoster virus (VZV), primarily affects adults who have had chickenpox earlier. After chickenpox recovery, the virus remains dormant in certain nerve cells of the body, reactivating later in life as Shingles. Factors like aging, stress, certain medications, or weak immunity can increase the risk of reactivation.
Shingles present with a painful, blistering rash typically appearing in a band on one side of the body. It is accompanied by symptoms like tingling, itching, fever, and headache. |
Shingles usually resolve within weeks. However, complications such as postherpetic neuralgia, skin infections, and eye problems can arise, particularly in older adults or those with weakened immune systems.
Vaccination can prevent the condition. It is recommended for individuals 50 and older and 19 and older with weakened immune systems.
Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial for managing shingles and reducing its complications. Treatment focuses on reducing the virus's effects and managing pain. Covering the rash is vital to avoid virus transmission, especially to vulnerable groups like pregnant women and those with weakened immunity.
Key Facts
- Individuals above 50 years of age.
- Both men and women but more common in women
- India: 705 per million population per year (2023)
- Cellulitis
- Chickenpox
- Contact stomatitis
- Skin manifestations of herpes simplex
- Folliculitis
- Human cowpox infections
- Irritant contact dermatitis
- Insect bites
- Lichen striatus
- Candidiasis
- Medical history and physical examination
- Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) test
- Viral culture test
- Direct fluorescent antibody (DFA) test
- Antibody test: IgM antibody , IgG antibody
- Antiviral medications: Acyclovir, famciclovir, valacyclovir
- Topical antibiotics: Mupirocin or framycetin
- Pain management: acetaminophen or ibuprofen, codeine for severe pain
- Anticonvulsants: Gabapentin or pregabalin
- Antidepressants: Amitriptyline or nortriptyline
- Post-Herpetic Neuralgia management: Topical capsaicin, transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation or acupuncture, botulinum toxin into the affected area
- General physician
- Dermatologist
- Internal Medicine Specialist
- Infectious Disease Specialist
Symptoms Of Shingles
Shingles, also known as herpes zoster, is a viral infection caused by the varicella-zoster virus (VZV), the same virus responsible for chickenpox. Shingles affect the nerves and manifests through various symptoms.
Common symptoms of shingles typically develop in 3 stages and may include:
1. Prodrome (Early symptoms stage)
-
Symptoms may appear 1-4 days before the rash onset.
-
Early signs include localized tingling, itching, or burning sensations, often accompanied by intermittent stabbing pain.
-
Some individuals may experience systemic symptoms like tiredness, fever, headache, and enlarged lymph nodes in the affected area.
2. Infectious rash (Acute stage)
-
Lasting 7-10 days, the rash typically appears in a band or line on one side of the body, following the path of nerve fibers.
-
It may occur on the trunk, neck, forehead, or genitals, accompanied by pain.
-
The rash evolves from red lesions to blisters, and crusting over 1-2 weeks.
-
Rubbing or scratching the rash can lead to infectious lesions, potentially transmitting the virus.
3. Resolution (Healing stage)
-
Usually, within ten days of rash onset, lesions begin to crumble. This can last 2-4 weeks and may indicate the end of infection.
-
Healing may take longer in older or immunocompromised patients, with possible scarring or changes in skin color post-resolution.
Are shingles contagious?
-
Shingles patients are contagious once the blisters appear. Those who never had chickenpox or didn’t get the vaccine can get infected with VZV from someone who has shingles.
-
VZV can spread by direct contact with the fluid from shingles blisters or by breathing in virus particles from the blisters. If infected, people will get chickenpox, not shingles. However, they could develop shingles later in life.
-
Individuals suffering from chickenpox are more likely to spread VZV than individuals with shingles.
-
Covering rashes can lower the risk of spreading the virus.
Causes Of Shingles
Shingles, also known as herpes zoster, occur when the varicella-zoster virus (VZV), which is responsible for chickenpox, is reactivated.
Once an individual has recovered from chickenpox, the virus lies dormant in nerve tissues. This dormant state persists indefinitely, but if the virus reactivates, it manifests as Shingles. However, not everyone who has had chickenpox will experience shingles.
While the exact cause of shingles remains uncertain, it is often linked to age-related decline in immunity.
Boost your immune system's defenses against shingles with immune-boosting supplements.
Risk Factors For Shingles
Shingles, caused by the varicella-zoster virus, can affect anyone who has previously had chickenpox. Several factors increase the likelihood of developing shingles:
1. Age: Shingles primarily affects older adults, with those over 50 at higher risk due to age-related weakening of immunity.
2. Stress: Elevated stress levels can weaken immunity, making the body more susceptible to viral infections like shingles.
3. Weakened immunity: Certain conditions, such as cancer and HIV/AIDS, can compromise the immune system, elevating the risk of shingles.
4. Immunosuppression: Long-term use of immunosuppressive medications in the following cases can predispose to shingles:
- Radiation or chemotherapy for cancer treatment
- Organ transplant
- Severe psoriasis or advanced psoriatic arthritis
5. Recent trauma or injury: Physical trauma or injury to the skin can sometimes trigger the reactivation of the varicella-zoster virus, leading to shingles in the affected area.
Diagnosis Of Shingles
Shingles are usually easy to recognize and diagnose due to their classic skin rashes. Diagnosis typically involves a combination of medical history and physical examination.
Testing for the varicella-zoster virus (VZV) involves analyzing blood, fluid, or tissue samples using various methods:
-
Medical history: The healthcare provider will inquire about symptoms, including any pain, tingling, or rash, as well as any recent illnesses or exposures.
-
Physical examination: The doctor will examine the rash and affected skin area. Shingles typically present as a unilateral (on one side of the body), painful, and blistering rash that follows a dermatomal distribution (in a band or strip along a specific nerve pathway).
-
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) test: This test detects genetic material from VZV in a sample, often obtained by swabbing open blisters. PCR is highly accurate and provides rapid results, making it the preferred method for confirming VZV infection.
-
Viral culture test: Cells from a swab sample are cultured in a laboratory to detect VZV presence. While this test is useful, it is less accurate compared to PCR.
-
Direct fluorescent antibody (DFA) test: This test, conducted on swab samples, employs a fluorescent dye and specialized microscope to identify VZV. Although it yields rapid results, it is not as precise as PCR.
-
Antibody test: This blood test detects antibodies produced against VZV. IgM antibody testing indicates current or recent VZV infection, while IgG antibody testing reveals past exposure to VZV.
Suspecting shingles? Don't wait! Take our comprehensive diagnostic test.
Celebs affected
In 2013, pop sensation Justin Bieber announced via Twitter that he had been diagnosed with Shingles at the age of 19. He mentioned experiencing pain and discomfort, but he assured his fans that he was receiving medical treatment and would recover soon.
Renowned comedian and actress Roseanne Barr revealed her battle with Shingles in interviews, describing the pain and discomfort she experienced during the outbreak. She emphasized the importance of seeking timely medical intervention and advocated for greater awareness of the condition
Prevention Of Shingles
Preventing shingles primarily involves vaccination and healthy lifestyle habits to bolster immune function.
1. Get vaccinated against Shingles
The most effective method for preventing shingles is through vaccination.
SHINGRIX is a recombinant subunit vaccine designed to stimulate the immune system's production of antibodies against the varicella-zoster virus.
Studies show that two doses of Shingrix offer over 90% protection against shingles and its complications.
Who should get SHINGRIX?
CDC recommends two doses of recombinant zoster vaccine (RZV, Shingrix), separated by 2 to 6 months, to those who
-
Are 50 years and older.
-
Are 19 years and older with weakened immune systems due to immunodeficiency or immunosuppressive therapy.
Important Note:
SHINGRIX is not indicated for the prevention of primary varicella infection (Chickenpox).
Who should not get SHINGRIX?
-
Individuals with a history of a severe allergic reaction to any component of the vaccine or after a previous dose of Shingrix.
-
Vaccination may be postponed for pregnant or breastfeeding individuals or those experiencing an acute episode of shingles.
Learn more about SHINGRIX vaccine
2. Get timely treatment for Chickenpox
Timely treatment of Chickenpox is crucial for averting future complications like Shingles.
Antiviral medications can mitigate the severity and duration of the infection, lowering the risk of viral latency and subsequent reactivation.
Ensure your child receives Chickenpox vaccine at the recommended ages:
- First dose: 12-15 months old
- Second dose: 4-6 years old
- For individuals 13 years and older without prior Chickenpox or vaccination, two doses, spaced at least 28 days apart, are advised.
Is your next vaccination due? Consider TATA 1MG. Your trusted source to buy vaccines.
3. Avoid contact with individuals with chickenpox or shingles
Avoiding close contact with individuals having chickenpox or shingles can reduce the risk of exposure to the virus.
4. Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle
Adopting a healthy lifestyle can support immune function and reduce the risk of shingles.
Make sure to:
- Consume a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains.
- Engage in regular exercise to promote overall health and immune function.
- Manage stress through relaxation techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises.
- Get adequate sleep each night to support a healthy immune system.
Vitamin D supplements can enhance immunity in older adults. Studies show that supplementation increases immune response to viruses and reduces inflammation in the elderly, potentially improving their overall health.
Explore our wide range of vitamin D supplements today!
Doctor To Visit
In many instances, shingles symptoms resolve on their own; however, seeking early medical intervention can help manage the condition effectively. If symptoms persist or worsen, it's advisable to consult a healthcare professional.
Specialists who can assist in treating shingles include:
- General Physician
- Dermatologist
- Internal Medicine Specialist
- Infectious Disease Specialist
General physicians can diagnose and provide primary care for shingles. They may refer patients to specialists for further evaluation or treatment adjustments.
Dermatologists specialize in skin conditions and can provide expertise in diagnosing and treating shingles-related skin manifestations.
Internal medicine specialists can provide a comprehensive treatment plan for adults, particularly for complex cases of shingles or individuals with compromised immune systems.
Infectious disease specialists have expertise in managing diseases like shingles to minimize complications and improve outcomes.
Consult our professional doctors.
Treatment Of Shingles
Shingles typically resolve on its own within a few weeks. However, prompt treatment can help alleviate symptoms and reduce the risk of complications. Treatment approaches for shingles include:
1. Antiviral medications
Commonly prescribed antiviral medications include:
2. Topical antibiotics
Topical antibiotic creams such as Mupirocin or Framycetin may be recommended alongside antiviral therapy to prevent secondary bacterial infections.
3. Pain management
Various treatments can help alleviate shingles-related pain, including:
-
Application of cool compresses to the affected area
-
Use of medicated lotion or creams to soothe irritated skin
-
Numbing medications such as lidocaine
-
Rest and over-the-counter pain relievers like acetaminophen or ibuprofen
-
Prescription painkillers like codeine for severe pain
4. Anticonvulsants and tricyclic antidepressants
Certain medications were initially developed for other purposes but may be prescribed off-label to help alleviate nerve pain associated with post-herpetic neuralgia, such as:
-
Gabapentin or Pregabalin (Anticonvulsants)
-
Amitriptyline or Nortriptyline (Tricyclic antidepressants)
5. Post-Herpetic Neuralgia Management
Post-herpetic neuralgia, a common complication in elderly patients, can be managed with various treatments once the lesions have crusted. These include:
- Local anesthetic applications
- Topical capsaicin
- Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation or acupuncture
- Botulinum toxin into the affected area
Note: For elderly PHN patients intolerant to oral medications, topical therapies like Lidocaine 5% patch can provide relief.
Trust TATA 1MG as your one-stop destination for buying medications.
Do’s and Don'ts for Shingles
- Isolate during the contagious phase.
- Avoid Aspirin in children due to the risk of Reye's Syndrome (a rare but serious illness in children, linked to viral infections, causing liver and brain swelling).
- Please consult a doctor before using anti-inflammatory painkillers, as they can increase the risk of severe skin infections.
- Practice daily cleansing with warm water to help prevent secondary bacterial infections.
- Keep nails short, and consider wearing gloves to avoid scratching your skin.
Home-care For Shingles
1. Baths
- A 15-minute bath with cool water can ease shingles pain and itching.
- Daily bathing keeps skin clean to prevent infections.
- Use gentle, fragrance-free cleansers, and avoid harsh scrubbing.
- Pat dry with a clean towel and launder it promptly to prevent virus spread.
- Oatmeal baths can also provide relief from the burning and itching sensations of shingles.
2. Rash care
- Wash the rash with a fragrance-free cleanser daily.
- Apply a thin layer of clean petroleum jelly and cover it with a sterile, non-stick bandage.
- Wash hands after touching the rash.
- Do not let dressings or plasters stick to the rash.
- Avoid clothing or fabrics that may irritate the rash. Opt for loose, breathable clothing.
- Avoid using antibiotic cream. This may slow the healing process.
- Keep nails short to prevent scratching and minimize the risk of infection.
- After scabbing, relieve itching with calamine lotion.
3. Herbal remedies
The following herbal remedies may offer relief from shingles symptoms, but it's important to consult with a doctor before using them, especially if you're already receiving medical treatment.
- Turmeric (Haldi): Turmeric is known for its anti-inflammatory and immune-boosting properties. It may help reduce inflammation and promote healing of the shingles rash.
How to use: You can add turmeric powder to your food or drink turmeric tea by steeping fresh or dried turmeric rhizomes in hot water.
Buy turmeric products from TATA 1MG. - Chamomile flower: Chamomile has anti-inflammatory and soothing properties that can help relieve pain and inflammation associated with shingles.
How to use: You can make chamomile tea by steeping chamomile flowers in hot water and drinking it at least twice daily. - Licorice (Mulethi): Licorice root contains compounds with antiviral and anti-inflammatory properties, which may help reduce the severity and duration of shingles outbreaks.
How to use: You can prepare licorice root tea by simmering dried licorice root in water for 10-15 minutes and drinking it up to three times a day. - Passionflower leaf: Passionflower is known for its calming and soothing properties, which can help reduce stress and promote relaxation. It may also help relieve pain associated with shingles.
How to use: Passionflower tea can be prepared by steeping dried passion flower leaves in hot water and drinking it several times a day. - Calendula flower: Calendula has anti-inflammatory and wound-healing properties, which can help soothe and promote healing of the shingles rash.
How to use: Calendula cream or ointment can be applied topically to the affected area several times daily. It's essential to choose products made from high-quality calendula extract and consult a doctor before using calendula, especially if you have allergies or skin sensitivities.
4. General health measures
- Get adequate rest.
- Consume a healthy, well-balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals.
- Drink plenty of fluids to stay hydrated.
- Engage in enjoyable activities to distract from discomfort.
- Practice stress-reduction techniques such as meditation or deep breathing to minimize discomfort and promote healing.
5. Monitor your health
- Report any signs of infection, persistent pain after rash clearance, or feeling unwell to your doctor.
- Discuss the possibility of getting the shingles vaccine with your doctor after the rash has cleared.
6. Prevent transmission
- Cover the rash and avoid touching or scratching it.
- Limit close contact with individuals who have not had chickenpox or the varicella-zoster vaccine to prevent the spreading of the virus.
- Do not share towels, swim, play contact sports, or go to work or school if your rash is weeping (oozing fluid) and can’t be covered.
- Isolate from pregnant women, infants, sick individuals, and those without immunity to chickenpox until the rash has cleared to prevent transmission.
Interesting Fact!
Shingles during pregnancy do not harm the unborn baby as the mother already carries the virus. However, Chickenpox in pregnancy can be severe and requires immediate medical care to avoid complications for both mother and baby.
Complications Of Shingles
Shingles typically resolve within 2–4 weeks, but some individuals may encounter complications, including:
1. Postherpetic Neuralgia (PHN)
Even after the rash disappears, some may endure persistent pain in the affected area for over three months, known as Postherpetic Neuralgia (PHN).
PHN involves damaged nerve fibers sending exaggerated pain messages from the skin to the brain, resulting in prolonged nerve pain.
2. Eye problems
Shingles affecting the ophthalmic nerve (a nerve responsible for sensory innervation of the upper face and eye) can lead to various eye problems, collectively known as Herpes Zoster Ophthalmicus. If not treated in time, these problems may lead to
Quick Byte!
A shingles rash on your face constitutes a medical emergency as it could impact eyesight. Prompt medical attention is essential to safeguard your vision.
3. Ramsay hunt syndrome
This is a complication of shingles involving the facial nerve. It can cause
- Facial paralysis
- Hearing loss
- Vertigo
- A rash in the ear or mouth.
4. Skin infection
Scratching the shingles rash can lead to bacterial skin infection. This can cause additional discomfort and pain and may require antibiotic treatment.
5. White Patches or Scarring
After the shingles rash heals, some individuals may notice white patches in the affected area due to a loss of pigment (hypopigmentation) or scarring. These changes in skin appearance may be permanent.
Inflammation of various organs: While rare, shingles can lead to inflammation of the:
- Lungs (Pneumonia)
- Liver (Hepatitis)
- Brain (Encephalitis)
- Spinal cord (Transverse myelitis)
- The protective membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord (Meningitis)
These complications can be serious and may require hospitalization and intensive medical treatment.
6. Disseminated shingles
In people with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS or undergoing immunosuppressive therapy, the shingles rash can spread to other parts of the body, potentially causing widespread infection and complications.
Older adults are more prone to PHN and endure more severe and prolonged pain compared to younger individuals.
Consult with a doctor now to mitigate the risk of complications.
Alternative Therapies For Shingles
Several complementary and alternative therapies may be used to help alleviate the symptoms of shingles and promote overall well-being. However, it's essential to consult with a healthcare professional before trying any new treatment, especially if you're already receiving medical care for shingles.
Acupuncture
Acupuncturists will determine which pattern of shingles you are suffering from and choose the corresponding acupuncture points to treat the underlying energy imbalance.
It involves insertion of thin needles into specific points on the body to help alleviate pain and promote healing. It also strengthens your immune system to help fight off the virus and treat other symptoms you may be experiencing, such as nausea or headaches.
Living With Shingles
Living with shingles can significantly impact an individual's quality of life due to the physical discomfort, emotional distress, and disruption of daily activities.
Shingles can have both short-term and long-term impacts on quality of life.
Short-Term Impact
- Shingles often present with pain, tingling, or itching before the rash appears, making sleep difficult and affecting daily activities.
- Sensitivity of the affected area can lead to discomfort even with minimal contact, and the rash can become infected.
- Contagiousness during the rash phase requires avoiding contact with other individuals, leading to feelings of isolation.
Coping Strategies:
- Seek medical attention for symptom management and potential antiviral treatment.
- Practice good hygiene to prevent infection of the rash.
- Communicate with loved ones about the need for isolation and seek support from them during this time.
Long-Term Impact (Postherpetic Neuralgia - PHN)
- Postherpetic neuralgia (PHN) can result from damaged nerve fibers during a shingles outbreak, causing ongoing pain lasting for months or even years.
- Debilitating pain can interfere with daily tasks, leading to isolation, loneliness, and increased risk of depression or anxiety.
- If shingles affect certain areas of the body, such as the eye or ear, complications such as vision, hearing, and balance problems can occur.
Coping Strategies:
- Seek medical treatment for PHN management, including medications and pain management techniques.
- Stay socially connected despite the pain, engaging in activities that bring joy, and seeking support from friends and family.
- To reduce the risk of future outbreaks and complications, prioritize getting vaccinated against Shingles.
Frequently Asked Questions
References
- Johns Hopkins Medicine. Shingles [Internet]. [cited 2024 Mar 26]. Available from:
- BPAC. Herpes zoster (shingles) [Internet]. 2014 Mar [cited 2024 Mar 26]. Available from:
- American Academy of Dermatology Association. Shingles causes [Internet]. [cited 2024 Mar 26]. Available from:
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Shingles: Clinical Overview [Internet]. [cited 2024 Mar 26]. Available from:
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Shingles: Treatment [Internet]. [cited 2024 Mar 26]. Available from:
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. [cited 2024 Mar 26]. Available from:
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. [cited 2024 Mar 26]. Available from:
- NHS Inform. Shingles [Internet]. [cited 2024 Mar 26]. Available from:
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. [cited 2024 Mar 26]. Available from:
- ResearchGate. Herbs for Treating Herpes Zoster Infections [Internet]. [cited 2024 Mar 26]. Available from:
- Medwin Publishers. Can India let go the opportunity to minimize million shingles cases annually as India launches shingrix zoster vaccine in April 2023? [Internet]. [cited 2024 Mar 26]. Available from: