- TOP CITIES
- New Delhi
- Gurgaon
- Pune
- Mumbai
- Bengaluru
- Kolkata
- Hyderabad
- Ahmedabad
- Chennai
- Indore
- Lucknow
- Jaipur
- Chandigarh
- Bhopal
- Noida
- Navi Mumbai
- Surat
- Patna
- Ludhiana
- Bhubaneshwar
- ALL CITIES
- Abohar
- Adad
- Adilabad
- Adoni
- Adsaidnakda
- Agar
- Agartala
- Agra
- Ahmedabad
- Ahmednagar
- Aizawl
- Ajmer
- Akola
- Aksjdhbaskjda
- Alappuzha
- Aligarh
- Alipurduar
- Alirajpur
- Allahabad
- Almora
- Alwar
- Ambala
- Ambattur
- Ambedkar Nagar
- Amravati
- Amreli
- Amritsar
- Amroha
- Anand
- Anantapur
- Ananthnag
- Anantnag
- Angamally
- Angul
- Ankleshwar
- Annur
- Anuppur
- Arakkonam
- Arambag
- Arantangi
- Araria
- Arcot
- Ariyalur
- Arwal
- Asansol
- Asdbakda
- Ashok Nagar
- Assaudh
- Attuvampatti
- Auraiya
- Aurangabad Bihar
- Aurangabad Maharashtra
- Aviyur
- Ayyangarkulam
- Azamgarh
- Badlapur
- Bagalkot
- Bageshwar
- Baghpat
- Bagpat
- Bahadurgarh
- Bahraich
- Baksa
- Balaghat
- Balangir
- Baleswar
- Ballia
- Bally
- Balrampur
- Banaskantha
- Banda
- Bangalore
- Bangalore Rural
- Banka
- Bankura
- Banswara
- Barabanki
- Baramati
- Baramulla
- Baran
- Baraut
- Bardhaman
- Bareilly
- Bargarh
- Barmer
- Barnala
- Barpeta
- Barrackpore
- Baruipur
- Barwani
- Basirhat
- Bastar
- Basti
- Bathinda
- Beawar
- Beed
- Begumganj
- Begusarai
- Behraghora
- Behrampur
- Belgaum
- Bellary
- Belur
- Bengaluru
- Betul
- Betul Ganj
- Bhadrak
- Bhadravati Karnataka
- Bhagalpur
- Bhandara
- Bharatpur
- Bharuch
- Bhatkal
- Bhavani
- Bhavnagar
- Bhilai
- Bhilwara
- Bhind
- Bhiwadi
- Bhiwandi
- Bhiwani
- Bhojpur
- Bhopal
- Bhubaneshwar
- Bhuna
- Bhusawal
- Bidar
- Bijapur Chattisgarh
- Bijapur Karnataka
- Bijnor
- Bikaner
- Bilaspur Chattisgarh
- Bilaspur Himachal Pradesh
- Birbhum
- Bishnupur
- Boisar
- Bokaro
- Bongaigaon
- Bongaon
- Botad
- Boudh
- Budaun
- Budgam
- Bukkapatnam
- Bulandshahr
- Buldana
- Buldhana
- Bundi
- Burdwan
- Burhanpur
- Buxar
- Cachar
- Calicut
- Chamarajanagar
- Chamba
- Chamoli
- Champawat
- Champhai
- Chandauli
- Chandel
- Chandigarh
- Chandrapur
- Changanassery
- Changlang
- Chatra
- Chennai
- Chhatarpur
- Chhindwara
- Chikkaballapur
- Chikkaballapura
- Chikmagalur
- Chintamani
- Chitradurga
- Chitrakoot
- Chittoor
- Chittorgarh
- Chrompet
- Churachandpur
- Churu
- Cochin
- Coimbatore
- Cooch Behar
- Cuddalore
- Cuddapah
- Cuttack
- Dadra & Nagar Haveli
- Dahanu
- Dahod
- Dakshina Kannada
- Daman
- Damoh
- Dans
- Dantewada
- Darbhanga
- Darjiling
- Darrang
- Datia
- Dausa
- Davangere
- Debagarh
- Dehradun
- Delhi
- Deoghar
- Deoria
- Dera Bassi
- Devanahalli
- Dewas
- Dhakaoli
- Dhalai
- Dhamtari
- Dhanbad
- Dhar
- Dharmapuri
- Dharwad
- Dhemaji
- Dhenkanal
- Dholpur
- Dhone
- Dhubri
- Dhule
- Dhully
- Dibang Valley
- Dibrugarh
- Dibrugarh Tamil Nadu
- Dimapur
- Dindigul
- Dindori
- Dispur
- Diu
- Doda
- Dombivli
- Dombivli Station
- Dumka
- Dungarpur
- Durg
- Durgapur
- East Champaran
- East Garo Hills
- East Godavari
- East Kameng
- East Khasi Hills
- East Midnapore
- East Nimar
- East Siang
- East Sikkim
- East Singhbhum
- Ellanaickenpatti
- Ernakulam
- Erode
- Etah
- Etawah
- Faizabad
- Faridabad
- Faridkot
- Farrukhabad
- Fatehabad
- Fatehgarh Sahib
- Fatehpur
- Fazilka
- Fewf
- Fewp
- Firozabad
- Firozpur
- Gadag
- Gadarwara
- Gadchiroli
- Gajapati
- Gandhinagar
- Ganganagar
- Gangtok
- Ganjam
- Garhwa
- Gariaband
- Gautam Buddha Nagar
- Gaya
- Ghaziabad
- Ghazipur
- Gir Somnath
- Giridh
- Goa
- Goalpara
- Gobichettipalayam
- Godda
- Golaghat
- Golaniya
- Gonda
- Gondia
- Gopalganj
- Gopalmath
- Gorakhpur
- Greater Noida
- Greater Thane
- Gulbarga
- Gumla
- Guna
- Guntur
- Gurdaspur
- Gurgaon
- Guwahati
- Gwalior
- Hailakandi
- Halol
- Hamirpur Himachal Pradesh
- Hamirpur Uttar Pradesh
- Hansi
- Hanumangarh
- Hapur
- Harapanahalli
- Harda
- Hardoi
- Haridwar
- Hassan
- Hathras
- Haveri
- Hazaribag
- Hazaribagh
- Hdhd
- Hinauti
- Hindaun
- Hingoli
- Hisar
- Hojai
- Hooghly
- Hosakote
- Hoshangabad
- Hoshiarpur
- Hoskote
- Hospet
- Hosur
- Howrah
- Hubli
- Hyderabad
- Ichalkaranji
- Idukki
- Imphal
- Imphal East
- Imphal West
- Indore
- Itanagar
- Jabalpur
- Jagatsinghapur
- Jaintia Hills
- Jaipur
- Jaisalmer
- Jajapur
- Jalandhar
- Jalaun
- Jalgaon
- Jallipatti
- Jalna
- Jalore
- Jalpaiguri
- Jammu
- Jamnagar
- Jamshedpur
- Jamtara
- Jamui
- Janjgir-Champa
- Jashpur
- Jaunpur
- Jayamala
- Jehanabad
- Jhabua
- Jhai
- Jhajjar
- Jhalawar
- Jhansi
- Jhargram
- Jharsuguda
- Jhujhunu
- Jind
- Jodhpur
- Jorhat
- Junagadh
- Jyotiba Phule Nagar
- Kachchh
- Kadamakkudy
- Kadapa
- Kadiri
- Kadthal
- Kaghaz Nagar
- Kaimur Bhabua
- Kaithal
- Kakinada
- Kalahandi
- Kalipahari
- Kallakurichi
- Kalligudi
- Kalyani
- Kamal
- Kamrup
- Kanadukathan
- Kanchipuram
- Kandhamal
- Kandukur
- Kangra
- Kanker
- Kannauj
- Kannur
- Kanpur
- Kanpur Dehat
- Kanpur Nagar
- Kansapuram
- Kanyakumari
- Kapurthala
- Kar
- Karad
- Karaikal
- Karaikudi
- Karatholuvu
- Karauli
- Karbi Anglong
- Kargil
- Karimganj
- Karimnagar
- Karnal
- Karupatti
- Karur
- Karwar
- Kasaragod
- Kathua
- Katihar
- Katni
- Kattupakkam
- Kaushambi
- Kavaratti
- Kawardha
- Kendrapara
- Kendujhar
- Khagaria
- Khammam
- Khandwa
- Khanna
- Kharagpur
- Khargone
- Kheda
- Kheri
- Khorda
- Kichha
- Kinnaur
- Kiphire
- Kishanganj
- Kochi
- Kodagu
- Kodaikanal Observatory
- Koderma
- Kohima
- Kokrajhar
- Kolar
- Kolasib
- Kolhapur
- Kolkat
- Kolkata
- Kollam
- Kooram
- Koppal
- Koraput
- Korba
- Koriya
- Kota
- Kothakudi
- Kothur
- Kottayam
- Kovilpatti
- Koyilandy
- Kozhikode
- Krishna
- Krishnagiri
- Kulgam
- Kullu
- Kumbakonam
- Kumburvayal
- Kundli
- Kupwara
- Kurnool
- Kurukkalpatti
- Kurukshetra
- Kurung Kumey
- Kushinagar
- Kutch
- Laddivadi
- Lahul & Spiti
- Lakhimpur
- Lakhisarai
- Lakshadweep
- Lalitpur
- Lambakheda
- Latehar
- Latur
- Lawngtlai
- Leh
- Lohardaga
- Lohit
- Lonavala
- Longleng
- Lower Dibang Valley
- Lower Subansiri
- Lucknow
- Ludhiana
- Lunglei
- Machur
- Madhepura
- Madhubani
- Madhupur
- Madikeri
- Madurai
- Mahabubabad
- Mahabubnagar
- Mahadanapuram
- Maharajganj
- Mahasamund
- Mahbub Nagar
- Mahe
- Mahendragarh
- Mahoba
- Mainaguri
- Mainpuri
- Majuli
- Malappuram
- Malda
- Malkangiri
- Malout
- Mammit
- Manakudi
- Manapparai
- Manawar
- Mandi
- Mandi Gobindgarh
- Mandla
- Mandsaur
- Mandya
- Mangalore
- Manipal
- Mannargudi
- Mansa
- Margao
- Marigaon
- Mathura
- Mau
- Mayurbhanj
- Medak
- Meenkashipuram
- Meerut
- Mehsana
- Melaparuthigudi
- Melpallam
- Melpattamkarisalkulam
- Melvisharam
- Midnapore
- Mirzapur
- Moga
- Mohali
- Mohanur
- Mokokchung
- Mon
- Moradabad
- Morena
- Muchipara
- Mughal Sarai
- Muktsar
- Mumbai
- Mumbai Extension
- Munger
- Murshidabad
- Muzaffarnagar
- Muzaffarpur
- Mysore
- Nabarangapur
- Nadia
- Nadiad
- Naduvakurichi
- Nagaon
- Nagapattinam
- Nagaur
- Nagpur
- Naidupuram
- Nainital
- Najibabad
- Nalanda
- Nalbari
- Nalgonda
- Namakkal
- Nanded
- Nandurbar
- Narayanpur
- Narmada
- Narnaulajsbd
- Narsinghpur
- Narsipatnam
- Nashik
- Navi Mumbai
- Navsari
- Nawada
- Nawanshahr
- Naxalbari
- Nayagarh
- Neemrana
- Neemuch
- Neeraj
- Nelamangala
- Nellore
- Nerur
- New Delhi
- New Kk
- Nicobar
- Nilgiri
- Nilgiris
- Nizamabad
- Noida
- North 24 Parganas
- North And Middle Andaman
- North Cachar Hills
- North Dinajpur
- North Goa
- North Sikkim
- North Tripura
- Nowda
- Nuapada
- Nuh
- Nuvem
- Ooty
- Osmanabad
- Pakur
- Palakkad
- Palamalai
- Palamu
- Palani
- Palghar
- Pali
- Pambakovil Shandy
- Pamjis
- Panaji
- Panchkula
- Panchmahal
- Panipat
- Panna
- Panvel - Station
- Papanasam
- Pappankulam
- Pappinaickenpatti
- Papum Pare
- Paradip
- Parbhani
- Pasumpon
- Patan
- Pathanamthitta
- Pathankot
- Patiala
- Patna
- Pauri Garhwal
- Pavitram
- Perambalur
- Peren
- Phalghat
- Phek
- Pilani
- Pilibhit
- Pinnathur
- Pithoragarh
- Pondicherry
- Ponga
- Poonamalle
- Poonch
- Porbandar
- Port Blair
- Prakasam
- Pratapgarh
- Proddatur
- Pudukkottai
- Pulankurichi
- Pulavadi
- Puludipatti
- Pulwama
- Pune
- Pungamuthur
- Purba Bardhaman
- Purbasthali
- Puri
- Purnia
- Puruliya
- Puzhal
- Quilon
- Raebareli
- Raichur
- Raigad Maharashtra
- Raigarh Chattisgarh
- Raikasba
- Raipur
- Raisen
- Rajahmundry
- Rajauri
- Rajgangpur
- Rajgarh
- Rajkot
- Rajnandgaon
- Rajpura
- Rajsamand
- Ramanagar
- Ramanathapuram
- Ramgarh
- Ramjas
- Rampur
- Ranchi
- Rangareddi
- Rangareddy
- Ranipet
- Rash
- Rasho
- Ratlam
- Ratnagiri
- Raurkela
- Rayagada
- Reasi
- Rewa
- Rewari
- Ri Bhoi
- Rishikesh
- Rohtak
- Rohtas
- Roorkee
- Ropar
- Rourkela
- Rudraprayag
- Rudrapur
- Rupnagar
- Rurka Kalan
- S.A.S. Nagar
- Sabarkantha
- Saegama
- Sagar
- Saharanpur
- Saharsa
- Sahibganj
- Saiha
- Salem
- Samastipur
- Sambalpur
- Sambhal
- Sangareddy
- Sangli
- Sangrur
- Sant Kabir Nagar
- Sant Ravidas Nagar
- Saran
- Sare
- Sarega
- Saregamapa
- Satara
- Satna
- Sawai Madhopur
- Secunderabad
- Sehore
- Senapati
- Seoni
- Seraikela-Kharsawan
- Serchhip
- Shahapur
- Shaharanpur
- Shahdol
- Shahjahanpur
- Shahpura
- Shajapur
- Shamshabad
- Sheikhpura
- Sheohar
- Sheopur
- Shikohabad
- Shillong
- Shimla
- Shimoga
- Shivpuri
- Shrawasti
- Shyamnagar
- Sibmandir
- Sibsagar
- Siddharthnagar
- Sidhi
- Sihora
- Sikar
- Siliguri
- Silvassa
- Simdega
- Simga
- Sindhudurg
- Singrauli
- Sirkaali
- Sirmaur
- Sirohi
- Sirsa
- Sitamarhi
- Sitapur
- Sivaganga
- Sivakasi
- Sivasagar
- Siwan
- Solan
- Solapur
- Sonapur
- Sonarpur
- Sonbhadra
- Sonipat
- Sonitpur
- Soro
- South 24 Parganas
- South Andaman
- South Dinajpur
- South Garo Hills
- South Goa
- South Sikkim
- South Tripura
- Sricity
- Srikakulam
- Srinagar
- Subarnapur
- Sujangarh
- Sultanpur
- Sundergarh
- Supaul
- Surat
- Surendranagar
- Surguja
- T Pudupatti
- Tadipatri
- Talasari
- Tamenglong
- Tapi
- Tarn Taran
- Tawang
- Tehri Garhwal
- Tenkasi
- Thane
- Thanjavur
- The Dangs
- Theni
- Thimmarajanpettai
- Thirukkalukundram
- Thirukkannamangaikottam
- Thiruvaiyaru
- Thiruvarur
- Thoothukudi
- Thoubal
- Thrissur
- Thungavi
- Tikamgarh
- Timarni
- Tinsukia
- Tirap
- Tiruchendur
- Tiruchirappalli
- Tiruklalikundram
- Tirumani
- Tirunelveli
- Tirupati
- Tiruppur
- Tirupur
- Tirur
- Tiruttani
- Tiruvalla
- Tiruvallur
- Tiruvannamalai
- Tiruvarur
- Titilagarh
- Tohana
- Tonk
- Trimulgherry
- Trivandrum
- Tuensang
- Tumkur
- Turaiyur Koitpatti
- Tuticorin
- Udaipur Rajasthan
- Udaipur Tripura
- Udayarpalayam
- Udham Singh Nagar
- Udhampur
- Udupi
- Ujjain
- Ukhrul
- Umaria
- Una
- Unnao
- Upper Siang
- Upper Subansiri
- Uttara Kannada
- Uttarkashi
- Vadagarai
- Vadakara
- Vadodara
- Vaishali
- Valsad
- Vandavasi
- Vapi
- Varanasi
- Vattur
- Vellore
- Vidisha
- Vijayawada
- Vikarabad
- Villupuram
- Virudhunagar
- Visakhapatnam
- Visalakshi Nagar
- Vizianagaram
- Warangal
- Wardha
- Washim
- Wayanad
- West Champaran
- West Garo Hills
- West Godavari
- West Kameng
- West Khasi Hills
- West Midnapore
- West Nimar
- West Siang
- West Sikkim
- West Singhbhum
- West Tripura
- Wokha
- Y.S.R.
- Yadgir
- Yamunanagar
- Yavatmal
- Zunhebotto
- BP Monitors
- Masks (N95, Surgical and more)
- Surgical Masks
- Face Shield
- N95 Masks
- N99 Masks
- Nebulizers & Vaporizers
- Oximeters & Pedometers
- Vital Signs Monitors & Wearables
- Oxygen Concentrators & Cans
- Weighing Scales
- Thermometers
- IR Thermometers
- Body Massager
- Diabetes Monitors
- Mobility Equipments
- Exercise Equipments
- Doctor's Corner
- Stethoscopes
- Tapes & Bandages
- Clinical Diagnostic Equipments
- Dressings & Wound Care
- Supports & Braces
- Neck & Shoulder Support
- Knee & Leg Support
- Back & Abdomen Support
- Ankle & Foot Support
- Hand & Wrist Braces
- Arm & Elbow Support
- Cervical Pillows
- Compression support & sleeves
- Heel support
- Vitamins & Supplements
- Multivitamins
- TestUdpTemporary
- Vitamins A-Z
- Mineral Supplements
- banner
- Nutritional Drinks
- Adult Daily Nutrition
- Kids Nutrition (2-15 Yrs)
- For Women
- Health Food & Drinks
- Green Tea & Herbal Tea
- Herbal Juice
- Apple Cider Vinegar
- Healthy Snacks
- Protein Supplements
- Whey Protein
- Amino Acids
- Mass Gainers
- Workout Essential
- Fat Burners
- Ayurveda Top Brands
- Dabur
- Sri Sri Tattva
- Baidyanath Products
- Kerala Ayurveda
- Jiva Ayurveda
- Tata 1mg Herbal Supplements
- Patanjali
- test_udp
- test_udp_1
Want to know more?
Read Our Editorial PolicyHave issue with the content?
Report Problem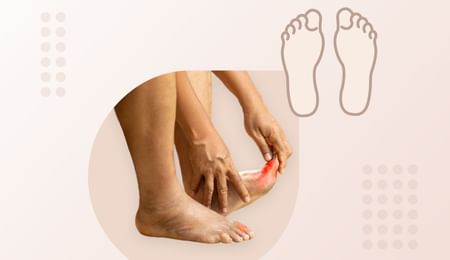
Gout
Overview
Gout is one of the most common and painful forms of arthritis. It causes inflammation in the joints due to high levels of uric acid in the body. Uric acid is a waste product which in excess can lead to accumulation in the form of urate crystals in the joints.
The symptoms of gout include swelling and redness in joints along with sudden sharp pain. The most common area to be affected by high uric acid is the joint at the base of the big toe. Gout in feet is immensely tender and painful that even a mere touch on the swollen area becomes unbearable.
Gout often causes a burning sensation with severe pain that often results in an emergency visit to the hospital. However, with early detection and keeping the uric acid levels under control, gout can be controlled without much suffering.
In addition to medicines, diet also plays a key role in the management of gout. Some beneficial foods to eat with gout include green leafy vegetables, fruits, legumes, etc. Eggs and low-fat dairy products like slim milk and yogurt also qualify as foods good for arthritis and gout.
Key Facts
- Adults between 40-60 years of age
- Both men and women
- Joints
- Knee
- Foot
- Wrist
- Elbow
- Hand
- Septic arthritis
- Stress fracture
- Pseudogout
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Cellulitis
- Psoriatic arthritis
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): Naproxen, Indomethacin, Ibuprofen & Celecoxib
- Corticosteroids:Dexamethasone, Methylprednisolone, Prednisolone, Prednisone & Triamcinolone
- Colchicine
- IL-1 blockers: Canakinumab
- Xanthine oxidase inhibitors (XOI): Allopurinol & Febuxostat
- Urate lowering drugs: Losartan, Flurbiprofen & Probenecid
- Uricosurics: Sulfinpyrazone & Benzbromaron
- Rheumatologist
- Orthopedician
Causes Of Gout
Gout arises from deposition of urate crystals in joints. Urate crystals are formed due to high levels of uric acid in the body. Uric acid is formed by the breakdown of purine in the body. Purine is a natural substance found in the body. It is also found in certain foods.
Usually, uric acid is excreted via the kidneys into the urine. However due to overproduction of uric acid or reduced excretion of uric acid, it can build up, forming sharp, needlelike urate crystals. Once the blood is saturated with urate crystals, they are deposited in the bones and joints leading to pain, inflammation and swelling. The main factors affecting serum urate concentration include:
Overproduction of uric acid
This condition is known as hyperuricemia, where uric acid level in the blood rises above the normal i.e. 6.8 mg/dL (milligrams per deciliter). The causes include:Diet: Foods rich in purines such as cooked or processed food from animal and seafood origin is a key element of increasing uric acid precursors. They are:
- Red meat
- Fish
- Alcohol (particularly beer and spirits)
Endogenous urate production: Turnover of urate crystals increases in the following conditions:
- Chronic haemolytic anemia
- Haemoglobinopathies
- Secondary polycythaemia
- Thalassaemia
- Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency,
- Lesch-Nyhan syndrome
- Malignancies (cancer)
- Lead poisoning
Drugs: Some drugs are linked with overproduction of uric acid. These include:
- Diuretics
- Low dose salicylates
- Pyrazinamide
- Ethambutol
- Cytotoxics
Decreased excretion of uric acid
Most urate excretion occurs in the kidneys while the rest is excreted through the gastrointestinal tract (GIT). Reduced renal excretion is seen in the following:
-
Sickle cell anemia
-
Hyperparathyroidism
-
Chronic renal disease
On the basis of causes, gout can be classified into two categories, namely:
-
Primary gout: That is caused due to either overproduction or underexcretion of the uric acid.
-
Secondary gout: That is caused due to chronic kidney disease or prolonged medications affecting the kidney’s ability to remove uric acid from the body .
Stages of gout
Gout can progress in four stages, starting with asymptomatic gout under which the individual experiences no symptoms of the medical condition; however, the levels of uric acid keep on increasing in the body.
This stage is followed by the acute gout stage, accompanied by symptoms of severe pain and redness and can last for a few weeks.
The third stage is intercritical gout wherein recurring gout attacks are experienced without pain in between the attacks.
The final stage is chronic tophaceous gout, leading to other medical complications, especially kidney disease.
Symptoms Of Gout
An attack of gout generally happens overnight, which is so sharp and sudden that it often wakes up the affected person in the middle of the night with a burning sensation in the affected area. Acute gout attacks can last for somewhere between 3 and 10 days, and if you do not get the uric acid treatment in time, it can become chronic, causing permanent damage to your joints.
Some of the common symptoms and signs of high uric acid include:
1. Severe joint pain
Gout generally causes severe pain in the joint of the big toe, but the attack can occur in other joints as well, like the knee, ankle, foot, wrist, hand, and elbow or even fingers.
This pain is caused due to high uric acid in the joints, which can go out to the space between the bones and end up running against the soft lining of the joints, causing unbearable inflammation. This scenario is referred to as a gout attack. The pain is at peak within the first 4 to 12 hours of the attack and generally occurs either early morning or after midnight.
2. Prolonged discomfort
Even after the episode of the gout attack, the joint discomfort can last for days or weeks, but the pain gets subsidized. However, any gout attack in the future on the same joint generally lasts longer, causing sharper pain. Such later gout attacks can also affect other joints which were not affected in the previous strikes.
3. Swelling and redness
The area affected by gout swells up and becomes red with a feeling of tenderness, making it extremely sensitive to any sort of touch or weight over it. In cases of severe gout attacks, high uric acid can also turn the affected area purple in color.
4. Trouble in movement
As the gout attack becomes more frequent over one joint, high amounts of uric acid crystals get deposited in the joints. This reduces the ease of movement or the comfort of movement, which can also get converted into abnormal movement of the joints. This is one of the common high uric acid symptoms of chronic gout.
5. Tophi
The presence of high uric acid can lead to crystallization of the compound in the affected joint, resulting in the formation of small and firm lumps called tophi. These visibly large urate crystals are white and generally form near the toes, knees, elbow, fingers, wrist, or ears. Tophi, which generally occurs in the case of chronic tophaceous gout, can get swollen up to the point of a breakdown or burst and leak a pus-like fluid.
The fluid generally does not cause any pain but can prevent the affected person from doing normal activities on a day-to-day basis. In some cases, tophi can also potentially damage the cartilage and bone, leading to extreme pain while using the joint for routine activities.
In addition to the above-mentioned symptoms, another one of the common symptoms of gout in the ankle includes shiny and flushed skin. This is one of the externally visible symptoms, which can help you with gout’s early detection. Apart from this, there may also be a burning pain in the ankle.
Risk Factors For Gout
The root cause of gout is high uric acid concentration in the body, and thus the factors leading to a higher level of uric acid in the body are also the risk factors of gout, which primarily include:
Non- modifiable factors
1. Family history
If the history of gout attack runs through the family, then the chances of a person inheriting the genes, which makes it more likely that the kidney would not drain or urate the uric acid out of the body, increase, even if the kidneys are healthy. This happens especially when parents or grandparents have suffered from gout during their lifetime.
2. Gender and age
Men are more prone to developing gout as their body naturally contains a higher level of uric acid, and the risk is at its peak during the age of 30-50 years. Whereas for women, the levels of uric acid generally tend to be lower than that of males. However, after menopause, the concentration of uric acid in a female body reaches almost equivalent to that of a male body and puts them at an equivalent risk of developing gout.
3. Surgery or trauma
If an individual has undergone surgery or a traumatic experience, then the chances of developing gout increase. This is true especially in the case of an organ transplant due to the effects of the anti-rejection drugs prescribed to the patient after such surgical procedures.
4. Race/ethnicity
The risk of development of gout varies across populations according to race and ethnicity. According to studies, African Americans had a twofold increased risk of gout when compared to other people.
5. Genetic factors
Genetic aberrations in genes SLC22A12 SLC22A12 which are integral to uric acid absorption can also predispose to gout.
6. Other chronic diseases
Other ailments like high blood pressure, diabetes, heart diseases, and kidney-related diseases put an individual at a greater risk of being vulnerable to developing gout on top of foot, ankle joint, and other joints. Thus, if you are suffering from any medical condition, it is prudent that you consult a doctor to avoid the risk of developing gout further.
Modifiable factors
1. High purine diet
Food and beverages with high purine content like red meat, shellfish, or beer increase the risk of high levels of uric acid in the blood and, thus, the risk of developing gout. To reduce uric acid levels in your blood and avoid the risk of gout on top of foot or any other joint, you should ensure that you eat a balanced diet with low purine content.
2. Obesity
Being overweight increases the amount of uric acid produced by the body, which puts a lot of stress on the kidneys to excrete it. This often leads to saturation of uric acid in the blood due to the inability of the kidney to eliminate high levels of uric acid daily. Thus, to avoid the risk of gout, particularly chronic tophaceous gout, you must exercise and maintain an active physical regime to keep your body mass index (BMI) in check and reduce uric acid content in the body.
3. Certain medications
Some medications used to control hypertension or low dose aspirin or beta-blockers can also cause a higher level of uric acid concentration in the blood and hence increasing the risk of gout. Thus, it is always wise to check the side effects of your medications with your doctor before consuming them so that you can find a solution to reduce uric acid concentration in your body.
4. Alcohol consumption
Studies have reported that alcohol intake increases the risk of developing gout. Alcohol ingestion increases lactate levels which inhibit uric acid excretion via the kidneys. Alcohol also prompts purine degradation, leading to an increased uric acid level.
5. Fructose/sweetened- sugar beverages
Increased quantities of fructose and sugar-sweetened beverages (main sweetener being fructose) in the diet, contribution to gout.
Diagnosis Of Gout
A diagnosis of gout is usually simple as it is externally visible due to inflammation and redness of the skin of the affected joint. Any person experiencing symptoms like swelling, sharp pain, redness, and tenderness over their joints should consult a doctor to check the presence of gout and get the right uric acid treatment.
A diagnosis for gout is usually done in any of the following ways:
Physical examination
Depending upon the case, a doctor might be able to confirm the presence of gout via a physical examination of the patient as the effects of a gout attack are visible near and over the affected skin area. During physical examinations, the most commonly and easily found gout is gout on top of foot.
Blood test
-
Uric acid : This test checks the concentration of uric acid in the blood, which can hint toward the possibility of the presence of gout as the correlation between uric acid and gout is quite high. A uric acid level in the blood over 6.8 mg/dL (milligrams per deciliter) is high. However, not everyone with a high uric acid level has gout.
Urine test
-
Uric acid: The uric acid urine test can also be used to measure the level of uric acid in urine. A 24-hour urine sample is needed for the same.
Imaging tests
- X-ray of affected joint: The medical condition can also be detected with the help of an x-ray examination of the affected joint. An x-ray enables the doctors to check the presence of uric acid crystals as well as bone damages in the affected area.
- Ultrasound: Ultrasound is used for detection of joint effusion, synovitis (inflammation of soft tissues lining the joint spaces) and evaluation of cartilage, bone contour, and crystal deposition.
- Conventional CT (CCT): CT is characterized by excellent resolution and high contrast, hence it is the best technique for the assessment and characterization of urate crystals.
- Dual-energy CT (DECT): This new imaging technique for diagnosis of gout that allows the differentiation of deposits.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): MRI helps in assessment of inflammation, synovial thickening and erosion of joints.
- Nuclear scintigraphy: It uses very small, tracer amounts of radioactive molecules to diagnose diseases involving bone and soft tissues.
- Positron emission tomography (PET): This technique is helpful when gout presents at unusual locations.
Other tests
-
Synovial fluid analysis: Synovial fluid is a thick, straw-colored liquid found in small amounts in the joints. Its analysis helps to diagnose and treat joint problems like Gout.
-
Synovial biopsy: Synovial membrane refers to the tissue lining a joint. The examination of this tissue helps in diagnosing gout, or rule out other infections.
Here’s more on what uric acid test means and what the results indicate.
Celebs affected
Prevention Of Gout
Gout can be prevented in several ways, usually, a combination of such ways can lead to a reduced level of uric acid in the body and hence gout pain relief. Some of the ways in which you can relieve gout knee pain, gout pain in foot, and other joints are:
1. Avoid or limit alcohol
Alcohol consumption impacts the ability of the body to excrete uric acid from the system, which as a result increases the concentration of uric acid in the blood and poses a greater threat of developing or undergoing a gout attack. Similarly, fructose-sweetened drinks also cause the same condition, and hence their consumption should be either avoided or limited to reduce the risk of gout.
2. Increase intake of water
Increasing water consumption aids the kidney in flushing out the uric acid with urine and hence, reducing the chances of developing urate crystals in the body. However, the ideal amount of water consumption varies on an individual basis, depending upon their age, sex, level of fitness, and other factors.
3. Maintain a healthy body weight
An individual with healthy body weight is less vulnerable to a gout attack, as obesity leads to a higher level of uric acid in the body, making the job of kidneys of flushing out the uric acid difficult. However, it is important to note that weight loss should not be sudden as it can cause other complications. You should aim for a gradual and steady weight loss journey that will help reduce the risk of developing gout.
4. Avoid a high purine diet
Certain food items naturally contain a higher level of purine, which can lead to a higher level of uric acid in the body. This is because purine is naturally broken down in the body to form uric acid. Food items like red meat, tuna, turkey, bacon, and alcoholic beverages should be either avoided or consumed in a limited quantity to avoid the risk of developing a higher concentration of uric acid in the blood. Foods good for arthritis and gout include nuts, olive oil, berries, dark leafy greens, garlic, and onion.
5. Avoiding certain medications
Medications like diuretics can cause hyperuricemia - which is a higher level of uric acid concentration in the blood. If someone is consuming such medications, they should consult their doctor to see if there is a replacement or substitute for such drugs. Otherwise, regular consumption of such drugs can lead to the formation of urate crystals in the body.
Specialist To Visit
Gout can lead to potential bone damages, and hence if a person experiences a sudden sharp gout pain in the foot or other joint along with redness and swelling, they should not ignore such gout symptoms and consult a doctor at the earliest.
Specialists that can help and consult with gout are:
- General physician
- Orthopediacian
- Rheumatologist
Consult India’s best doctors from the comfort of your place with a single click.
Treatment Of Gout
A gout pain relief can be treated on the basis of the following:
Treatment of gout attacks
1. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): These drugs reduce both pain and inflammation. However, in some cases they may cause side effects, including ulcers, bleeding, and stomach pain.
Some of the common examples of these drugs include:
2. Corticosteroid medications: Corticosteroids help reduce gout pain and inflammation. They are available as both oral pills and in the form of injections. Corticosteroids used for gout include:
-
Prednisone
3. Colchicine: This drug has been found to be effective in reducing inflammation which causes pain, swelling and other symptoms of gout. However, it is contra-indicated in severe cases of chronic kidney diseases.
4. IL-1 blockers: Canakinumab, a long lasting antibody to IL-1 beta, is considered for the management of gout flares in patients with frequent flares contraindicated to NSAIDs, colchicine and steroids (oral or injectable).
Treatment of chronic gout
1. Xanthine oxidase inhibitors (XOI): XOI works by inhibiting uric acid synthesis. This class includes:
2. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: Long term treatment with non-steroidal antiinflammatory drugs is sometimes used to prevent recurrent gout.
3. Urate lowering drugs: These drugs act by reducing serum urate concentration. Initiation of urate lowering drugs is associated with an increased risk of gout flares due to crystal mobilization. This should be explained to the patient before the treatment. These include:
4. Uricosurics: Uricosuric drugs should not be used in patients with significant kidney impairment or a history of kidney stones. Drugs used are:
-
Sulfinpyrazone
-
Benzbromaron
Home-care For Gout
Gout is a rare medical condition but is known to cause high levels of pain and discomfort. If someone at your home is suffering these sudden gout attacks and pain breakout, you can practice the following do’s and don’ts, especially to keep a check on food to eat with gout.
Do’s
-
Drink at least 9-10 glasses of water to keep yourself well-hydrated.
-
Include citric fruits such as orange and lemon in your diet.
-
Eat more cherries to reduce inflammation in the body.
-
Drink coffee to lower uric acid levels in the body.
-
Elevate your joint to reduce swelling.
-
Avoid taking stress as it increases the inflammation in the body.
Don’ts
❌ Do not consume alcohol
❌ Do not consume fructose-sweetened drinks
❌ Do not consume foods containing high levels of purine
❌ Do not delay seeking medical consultation for gout
❌ Do not starve yourself for losing weight
❌ Do not consume sugar-rich foods
Here’s more on what to eat and what to avoid in case of gout.
Complications Of Gout
Chronic tophaceous gout can lead to the following medical complications:
1. Joint damage and deformation
Chronic gout can lead to swelling in your joints, deformation of joints, permanent joint damage, as well as permanent movement disabilities. In severe cases, individuals suffering from gout pain in foot and other joints can also require joint replacement surgery.
2. Tophi
Lumps of urate crystals are called tophi. They harden the skin over and near the joints, damaging cartilage. In rare cases, Tophi can also occur on the ears. These pointed crystals usually do not cause gout pain in the foot or other joints but can cause severe damage, restricting their movement permanently.
3. Kidney stones
Uric acid and gout go hand in hand. Therefore, individuals suffering from gout are more vulnerable to developing kidney stones in their urinary tract as the kidneys filter the uric acid.
4. Kidney damage and chronic kidney diseases
As the uric acid passes through the kidneys, its high concentration can damage the organs and cause permanent damage, leading to various chronic kidney diseases (CKDs) such as loss of kidney function, glomerulonephritis, and chyluria.
5. Psychological and emotional breakdown
A chronic tophaceous gout can cause permanent walking issues due to chronic gout knee pain and discomfort in other joints. This can affect the mental and emotional well-being of individuals suffering from medical conditions. This can further lead to severe issues, including anxiety and depression. Thus, if you have been suffering from uric acid and gout issues, it is wise to reach out for medical help to maintain your physical and emotional health.
Alternative Remedies For Gout
You can make use of the following home remedies for gout pain relief and its treatment.
Naturotherapy
1. Cherries: Consumption of cherries, including strawberries, blueberries, red cherries, etc., help prevent gout attacks and relieve gout knee pain and discomfort in other affected joints.
2. Ginger (adrak): Ginger is a great culinary ingredient for reducing inflammation in joints. You can have ginger by grading it in veggies, tea, or you can even try having raw ginger. Studies have found ginger to be effective in reducing gout pain. It ranks significantly among the foods good for arthritis and gout.
3. Celery (ajmoda): Celery is known for treating urinary issues. You can consume its extract, sticks as well as seeds to reduce the inflammation in your joints.
4. Hibiscus (gudhal): Hibiscus is a traditional herb that can be consumed in tea or with your regular food to treat gout at home. The flower has been found to be potentially effective in reducing uric acid levels in the body.
5. Hot/cold packs: Applying hot or cold water bags may also help in reducing joint inflammation and pain caused due to gout.
6. Dandelion: Dandelion is a flowering plant known for improving the functioning of the kidneys and liver. Research has shown that consumption of its extract in tea or as a supplement may reduce uric acid levels in the body.
7. Lemon water: Drinking two liters of water with two freshly squeezed lemons helps reduce the levels of uric acid in the body. Lemon effectively reduces uric acid as it neutralizes and helps get some relief from the pain.
Yoga
Yoga poses can also help in management of gout. You can try the following yoga poses along with meditation to treat gout and get some relief from sudden pain:
1. Ardha matsyendrasana: The spinal twist pose can help reduce uric acid levels in the body. It can be performed by sitting with legs stretched in front and bending your left leg so that its heel touches your right hip. After this, place your right leg over your left knee and twist your waist, shoulder, and neck.
2. Dhanurasana: The bow pose can be performed by lying on your stomach with your knees and elbows folded backward to hold your ankles.
3. Salabhasana: The locust pose can be simply performed by lying on your stomach with your arms by your side. With the pose, keep inhaling and exhaling for at least 20 seconds.
4. Ananda balasana: The happy baby pose can be performed by lying on your back and bringing your knees close to your chest from front. Remember to keep your arms inside your knees during this pose and hold your big toes gently.
5. Viparita karani: The legs-up-the-wall pose can be performed by sitting next to a wall with legs spread and pressed against the wall. Lie on your back and breathe gently for around 5 minutes.
Traditional chinese medicine (TMC)
TMC has also been used as an alternative therapy for management of gout. The main mechanisms of TCM treatment for gout during the remission stage include:
-
Benefiting Qi ( the force that makes up and binds together all things in the universe)
-
Nourishing blood
-
Tonifying spleen and kidney
-
Inhibiting inflammatory factors in joint fluid
-
Reducing blood uric acid level
-
Promotion of uric acid excretion
-
Enhancing immune function
-
Blocking the sensation of peripheral nerves
However, TMC needs more research and in-depth studies for scientific backing.
Living With Gout
Living with gout can be painful and difficult. However, you can manage and reduce its effects by adopting the following lifestyle recommendations.
1. Follow your medication diligently: Medication plays a highly significant role in the treatment of gout. You should follow your medication schedule timely and without fail. Also, if you start experiencing relief after following the prescribed medication, you should not make the mistake of leaving the medication in between without seeking your doctor’s permission.
2. Check your uric acid levels every 6 months: You should monitor and keep a check on your uric acid levels. Ideally, you should check your uric acid concentration twice a year and maintain it below 6 milligrams per decilitre.
3. Maintain a healthy body weight: You should maintain healthy body weight as per your body mass index (BMI). However, you should not indulge yourself in fad diets as it can strain your health, resulting in adverse effects on your body instead of doing any good.
4. Follow a 30-minute walk regimen: You should follow a 30-40 minutes walk routine to keep your body movements functional. This will also help you in achieving your ideal body weight.
5. Drink at least 7-8 glasses of water: Drinking water may help remove excess uric acid from the blood. Ideally, you should drink at least 7-8 glasses of water in a day to keep yourself hydrated.